


主管单位:中国科学技术协会
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



兵工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (S1): 152-159.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0731
收稿日期:2023-08-08
上线日期:2023-12-08
通讯作者:
基金资助:
ZHANG Zhonghao1, WANG Wei1,*( ), ZHANG Guokai2, WANG Zhen2, WU Gu3
), ZHANG Guokai2, WANG Zhen2, WU Gu3
Received:2023-08-08
Online:2023-12-08
摘要:
混凝土作为普遍使用的建筑材料,为进一步探索其在受到高温冷却后劣化损伤性能,使用ϕ74mm大口径分离式霍普金森压杆对不同温度冷却处理后的C30混凝土材料进行动态力学性能试验,得到其不同温度后、不同应变率下的应力-应变曲线,并针对其动态抗压强度、损伤变量及破碎形态进行了探讨。结果表明:在100~200℃范围内,混凝土的动态抗压性能下降有限,但当温度达到400℃及以上时,其力学性能下降明显,破碎形态严重。过高的温度会对混凝土材料造成损伤,高温冷却会使混凝土产生应变软化效应,高应变率下混凝土材料也体现出了应变率强化效应。过多的裂缝扩展也一定程度上抑制了损伤变量的增长。在相同温度处理后,应变率越高会使混凝土试样破碎越严重。且过高的温度会加剧混凝土的劣化损伤。
中图分类号:
张仲昊, 汪维, 张国凯, 王振, 吴汩. 不同高温作用后混凝土劣化损伤性能[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(S1): 152-159.
ZHANG Zhonghao, WANG Wei, ZHANG Guokai, WANG Zhen, WU Gu. Study on Deterioration and Damage Performance of Concrete at Different High Temperatures[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S1): 152-159.
| 成分 | 水泥 | 砂 | 碎石 | 水 | 粉煤灰 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 配合比 | 515 | 782 | 1271 | 175 | 57 |
表1 混凝土配合比
Table 1 Concrete mix ratio kg/m3
| 成分 | 水泥 | 砂 | 碎石 | 水 | 粉煤灰 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 配合比 | 515 | 782 | 1271 | 175 | 57 |
| 温度/℃ | 应变率/s-1 | 峰值应力/MPa |
|---|---|---|
| 66.2 | 27.97 | |
| 20 | 87.5 | 31.51 |
| 104.5 | 33.32 | |
| 69.5 | 26.82 | |
| 100 | 91.2 | 28.66 |
| 106.9 | 32.11 | |
| 72.1 | 24.49 | |
| 200 | 92.6 | 25.61 |
| 113.6 | 31.32 | |
| 73.7 | 24.91 | |
| 400 | 93.7 | 25.21 |
| 112.2 | 28.99 | |
| 70.9 | 15.48 | |
| 600 | 87.3 | 19.65 |
| 113.3 | 21.39 |
表2 混凝土试样测试相关结果
Table 2 Test results of concrete sample
| 温度/℃ | 应变率/s-1 | 峰值应力/MPa |
|---|---|---|
| 66.2 | 27.97 | |
| 20 | 87.5 | 31.51 |
| 104.5 | 33.32 | |
| 69.5 | 26.82 | |
| 100 | 91.2 | 28.66 |
| 106.9 | 32.11 | |
| 72.1 | 24.49 | |
| 200 | 92.6 | 25.61 |
| 113.6 | 31.32 | |
| 73.7 | 24.91 | |
| 400 | 93.7 | 25.21 |
| 112.2 | 28.99 | |
| 70.9 | 15.48 | |
| 600 | 87.3 | 19.65 |
| 113.3 | 21.39 |
| 温度/℃ | 自然冷却 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 颜色 | 裂纹 | 破损 | |
| 20 | 灰 | ||
| 100 | 灰、淡黄 | ||
| 200 | 灰、黄 | ||
| 400 | 灰白、淡红 | 细裂纹 | |
| 600 | 灰白、红 | 明显裂纹 | 少量剥落 |
表3 不同加热温度及冷却条件下混凝土试样外观对比
Table 3 Comparison of the appearances of concrete samples under different heating temperatures and cooling conditions
| 温度/℃ | 自然冷却 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 颜色 | 裂纹 | 破损 | |
| 20 | 灰 | ||
| 100 | 灰、淡黄 | ||
| 200 | 灰、黄 | ||
| 400 | 灰白、淡红 | 细裂纹 | |
| 600 | 灰白、红 | 明显裂纹 | 少量剥落 |
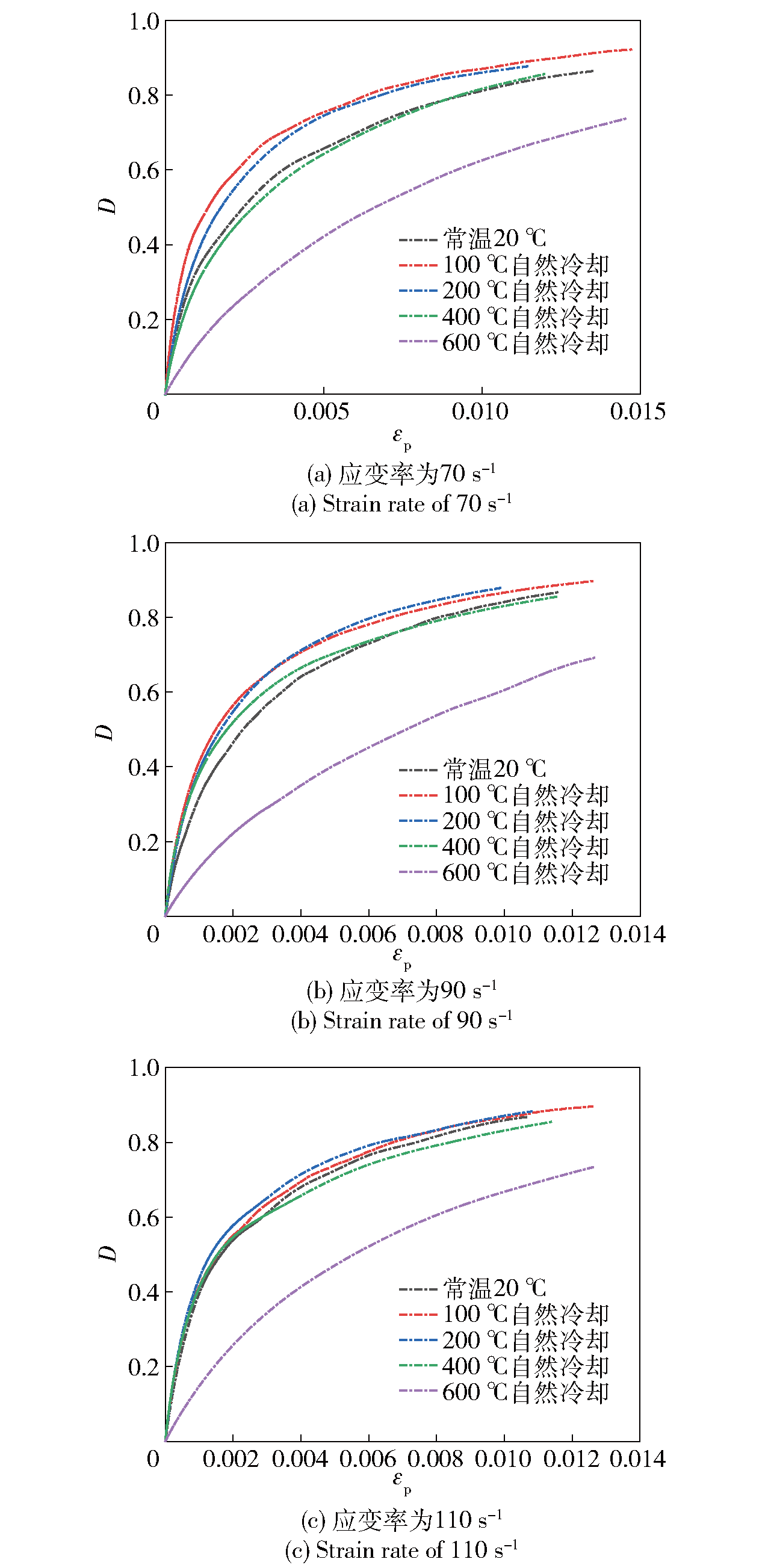
图8 相同应变率不同温度冷却后混凝土试样损伤变量与塑性应变的关系
Fig.8 Relationship between damage variable and plastic strain of concrete samples cooled at different temperatures with the same strain rate
| [1] |
方秦, 杨石刚, 陈力, 等. 天津港“8·12”特大火灾爆炸事故建筑物和人员损伤破坏情况及其爆炸威力分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2017, 50(3): 12-18.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
闫秋实, 任鹏程, 缪惠全. “克里米亚大桥”爆炸事件对我桥梁抗爆韧性研究的启示[J]. 防护工程, 2023, 45(2): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
江见鲸, 冯乃谦. 混凝土力学[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1991.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
王礼立, 王永刚. 应力波在用SHPB研究材料动态本构特性中的重要作用[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2005, 25(1): 17-25.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1039/C8RA00082D URL |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.10.011 URL |
| [7] |
李圣童, 汪维, 梁仕发, 等. 长持时爆炸冲击波荷载作用下梁板组合结构的动力响应[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(7): 138-149.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
汪维, 朱谢梅, 李磊, 等. 高强钢筋混凝土单向板在非接触爆炸下的抗爆性能研究[J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版), 2022, 35(6): 28-34.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.187 URL |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105715 URL |
| [11] |
吕天启, 赵国藩, 林志伸. 高温后静置混凝土力学性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2004, 25(1): 63-70.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
文彦博, 黄瑞源, 李平, 等. 高温高应变率下混凝土材料的损伤演化方程[J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(2): 54-63.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.3390/ma15176154 URL |
| [14] |
李启帆, 许金余, 赵德辉, 等. 基于分形理论的冲击荷载下钢纤维混凝土力学性能研究[J]. 防护工程, 2018, 40(6): 11-15.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128448 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2023.e01905 URL |
| [17] |
李胜林, 刘殿书, 李祥龙, 等. Ф75mm分离式霍普金森压杆试件长度效应的试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2010, 39(1): 93-97.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
卢芳云, 陈荣, 林玉亮, 等. 霍普金森杆实验技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
尹土兵. 考虑温度效应的岩石动力学行为研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.3.363 URL |
| [21] |
胡亮亮, 黄瑞源, 高光发, 等. 混凝土类材料SHPB实验中确定应变率的方法[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(6): 43-51.
|
|
doi: 10.1023/A:1022145201911 URL |
|
| [22] |
刘普, 王明华, 李庆涛. 高温后路缘石再生骨料混凝土的力学性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(12): 1233-1240.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.05.131 URL |
| [1] | 刘举, 张国凯, 王振, 姚箭, 李杰, 于思远, 纪玉国. 温压炸药近爆作用下RC梁破坏特征和毁伤规律试验研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(3): 864-874. |
| [2] | 康耕新, 颜海春, 张亚栋, 刘明君, 郝礼楷. 接触爆炸下混凝土墩破坏效应试验与数值模拟[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(1): 144-155. |
| [3] | 周广盼, 王荣, 王明洋, 丁建国, 张国凯. 涂覆聚脲混凝土自锚式悬索桥主梁抗爆性能试验与数值模拟[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(S1): 9-25. |
| [4] | 李旭, 岳松林, 邱艳宇, 王明洋, 邓树新, 刘念念. 近场水下爆炸气泡与混凝土组合板相互作用的试验研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(S1): 79-89. |
| [5] | 张丛琨, 张仲昊, 汪维, 李磊, 何翔. 超高强钢筋混凝土梁在静态加载下的抗弯性能试验[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(S1): 107-116. |
| [6] | 王佳, 尹建平, 李旭东, 伊建亚, 王志军. 基于量纲分析法的钢筋混凝土柱体缩比模型的构建[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(S1): 189-195. |
| [7] | 刘泓甫, 黄风雷, 白志玲, 段卓平. 刚性弹体带攻角斜侵彻贯穿混凝土靶板的理论模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(8): 2381-2390. |
| [8] | 苗飞超, 张向荣, 李东伟, 江涛, 周霖. 霍普金森压杆整形器模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(7): 1978-1984. |
| [9] | 马军, 汪旭光, 李祥龙, 王建国. 不耦合装药刻痕爆破裂纹的动态力学特征及损伤分形规律实验[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3676-3686. |
| [10] | 夏柳, 武伟超, 潘艾刚, 王亚飞, 王强, 闫伸. 单点及三点阵列毁伤模式对钢筋混凝土梁的毁伤效能比较[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3851-3861. |
| [11] | 李萌, 武海军, 董恒, 任光, 张鹏, 黄风雷. 基于机器学习的混凝土侵彻深度预测模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3771-3782. |
| [12] | 许迎亮, 刘彦, 闫俊伯, 白帆, 于浩, 李旭, 王虹富. 双装药同步爆炸钢筋混凝土梁毁伤效应[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3719-3732. |
| [13] | 亓晓鹏, 张杰, 赵婷婷, 王志勇, 王志华. 考虑骨料级配的混凝土靶板接触爆炸破坏模式[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3641-3653. |
| [14] | 宁建国, 杨帅, 李玉辉, 许香照. 低温/常温养护下混凝土的本构模型和抗爆试验[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(10): 2932-2943. |
| [15] | 蒋明飞, 许辉, 黄陈磊, 刘坤, 吴志林. 弹道明胶动态力学性能试验与本构模型研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(9): 2113-2120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4
京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4