


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 3465-3477.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0815
Special Issue: 群体协同与自主技术
Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Yan, DING Yuyan, ZHANG Xinglong, XU Xin*( )
)
Received:2022-09-07
Online:2023-05-12
Contact:
XU Xin
CLC Number:
JIANG Yan, DING Yuyan, ZHANG Xinglong, XU Xin. A Human-machine Collaborative Control Algorithm for Intelligent Vehicles Based on Model Prediction and Policy Learning[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(11): 3465-3477.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
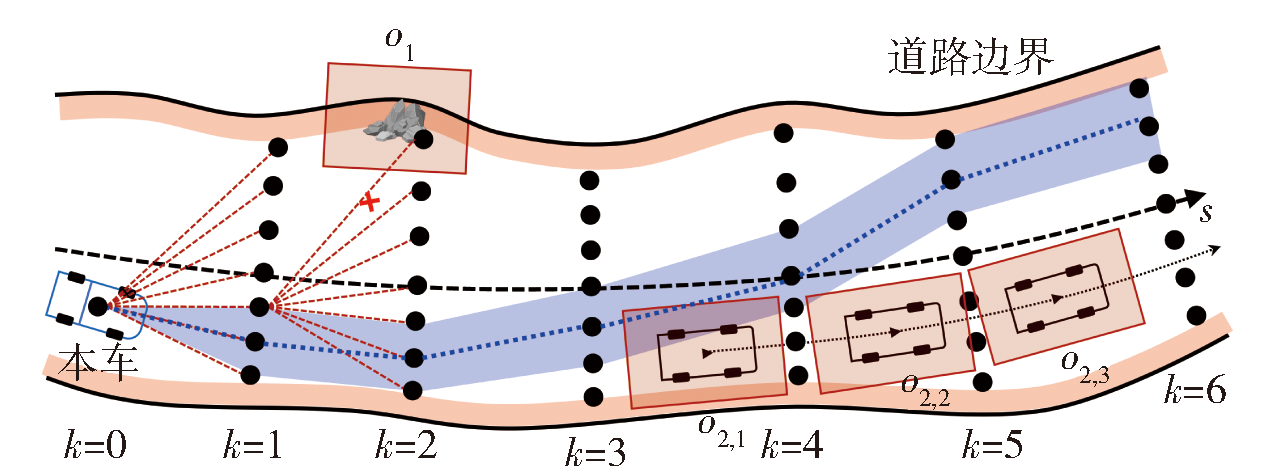
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of local driving route planning sprinkler sampling (o1 is a static obstacle, o2 is a dynamic obstacle, o2,k represents the polygonal envelope of obstacle 2 after collision processing at time k, and s is the direction of road centreline)
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| m/kg | 1555 | γ | 0.95 |
| hCG/m | 0.665 | ns | 15 |
| Ix/(kg·m2) | 846.6 | ζ | 1.1 |
| Iy/(kg·m2) | 1 816 | nd | 6 |
| Iz/(kg·m2) | 1 816 | Np | 30 |
| lf/m | 1.85 | Tp/s | 0.2 |
| lr/m | 1.80 | qc | 0.01 |
| Kϕ/(N·m·rad-1) | 51 600 | ql | 0.1 |
| Dϕ/(N·m·s·rad-1) | 5 300 | qω | 5.0 |
| Kθ/(N·m·rad-1) | 45 000 | 0.01 | |
| Dθ/(N·m·s·rad-1) | 2 600 | 0.5 | |
| Ccf/(N·rad-1) | 76 500 | 0.2 | |
| Ccr/(N·rad-1) | 76 500 | 1 | |
| w/m | 1.7 | Nc | 50 |
| ay,max/(m·s-2) | 4 | Tc/s | 0.02 |
| ay,min/(m·s-2) | -4 | imax | 5 |
| ax,max/(m·s-2) | -4 | /m | 0.2 |
| ax,min/(m·s-2) | -6 | 0.2 | |
| w1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | |
| w2 | 3.0 | 0.1 | |
| w3 | 0.5 | 10-9 | |
| w4 | 0.5 | 0.05 |
Table 1 Vehicle model parameters, and planner and controller parameters
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| m/kg | 1555 | γ | 0.95 |
| hCG/m | 0.665 | ns | 15 |
| Ix/(kg·m2) | 846.6 | ζ | 1.1 |
| Iy/(kg·m2) | 1 816 | nd | 6 |
| Iz/(kg·m2) | 1 816 | Np | 30 |
| lf/m | 1.85 | Tp/s | 0.2 |
| lr/m | 1.80 | qc | 0.01 |
| Kϕ/(N·m·rad-1) | 51 600 | ql | 0.1 |
| Dϕ/(N·m·s·rad-1) | 5 300 | qω | 5.0 |
| Kθ/(N·m·rad-1) | 45 000 | 0.01 | |
| Dθ/(N·m·s·rad-1) | 2 600 | 0.5 | |
| Ccf/(N·rad-1) | 76 500 | 0.2 | |
| Ccr/(N·rad-1) | 76 500 | 1 | |
| w/m | 1.7 | Nc | 50 |
| ay,max/(m·s-2) | 4 | Tc/s | 0.02 |
| ay,min/(m·s-2) | -4 | imax | 5 |
| ax,max/(m·s-2) | -4 | /m | 0.2 |
| ax,min/(m·s-2) | -6 | 0.2 | |
| w1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | |
| w2 | 3.0 | 0.1 | |
| w3 | 0.5 | 10-9 | |
| w4 | 0.5 | 0.05 |
| 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ttask | 完成驾驶任务总时长 |
| L2c | 车辆在违反安全区域边界情况下的行驶距离 |
| 转向操作做功,定义为 = ( + )dt |
Table 2 Performance indicators
| 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ttask | 完成驾驶任务总时长 |
| L2c | 车辆在违反安全区域边界情况下的行驶距离 |
| 转向操作做功,定义为 = ( + )dt |
| 方法 | 指标 | 测试人员 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 手动驾驶 | ttask/s | 268.4 | 244.9 | 247.9 | 233.5 | 227.7 | 248.1 |
| L2c/m | 190.2 | 6.0 | 29.0 | 56.8 | 96.9 | 173.7 | |
| 2945 | 2155 | 2089 | 2766 | 2587 | 1037 | ||
| 对比方法[ | ttask/s | 226.1 | 237.4 | 238.7 | 229.3 | 245.6 | 232.4 |
| L2c/m | 2.7 | 8.5 | 3.1 | 5.5 | 0 | 1.8 | |
| 1557 | 1157 | 1256 | 1564 | 1437 | 975 | ||
| 本文方法 | ttask/s | 224.6 | 217.9 | 234.8 | 218.9 | 234.5 | 217.4 |
| L2c/m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1717 | 914 | 1011 | 975 | 1168 | 852 | ||
Table 3 Statistics of performance indicators of different control methods in mountain road scene
| 方法 | 指标 | 测试人员 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 手动驾驶 | ttask/s | 268.4 | 244.9 | 247.9 | 233.5 | 227.7 | 248.1 |
| L2c/m | 190.2 | 6.0 | 29.0 | 56.8 | 96.9 | 173.7 | |
| 2945 | 2155 | 2089 | 2766 | 2587 | 1037 | ||
| 对比方法[ | ttask/s | 226.1 | 237.4 | 238.7 | 229.3 | 245.6 | 232.4 |
| L2c/m | 2.7 | 8.5 | 3.1 | 5.5 | 0 | 1.8 | |
| 1557 | 1157 | 1256 | 1564 | 1437 | 975 | ||
| 本文方法 | ttask/s | 224.6 | 217.9 | 234.8 | 218.9 | 234.5 | 217.4 |
| L2c/m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1717 | 914 | 1011 | 975 | 1168 | 852 | ||
| [1] |
陈慧岩, 陈舒平, 龚建伟. 智能汽车横向控制方法研究综述[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(6):1203-1214.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.06.021 |
|
|
|
| [2] |
胡云峰, 曲婷, 刘俊, 等. 智能汽车人机协同控制的研究现状与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7):1261-1280.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3154426 URL |
| [4] |
刘俊. 智能车辆人机协同转向控制策略研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020:13-29.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2865105 URL |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1109/TITS.6979 URL |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2018.04.007 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1080/00423114.2016.1256489 URL |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1049/itr2.v12.6 URL |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2200826 URL |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2555853 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/oca.v36.5 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2478857 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3167271 URL |
| [15] |
龚建伟, 姜岩, 徐威. 无人驾驶车辆模型预测控制[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2020.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114186 URL |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1002/oca.v36.5 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.073 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2021.106301 URL |
| [1] | LIU Jiangtao, ZHOU Lelai, LI Yibin. Trajectory Tracking and Obstacle Avoidance Control of Six-wheel Independent Drive and Steering Robot in Complex Terrain [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(1): 166-183. |
| [2] | LI Caoyan, GUO Zhenchuan, ZHENG Dongdong, WEI Yanling. Multi-robot Cooperative Formation Based on Distributed Model Predictive Control [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S2): 178-190. |
| [3] | CAO Zijian, SUN Zelong, YAN Guochuang, FU Yanfang, YANG Bo, LI Qinjie, LEI Kailin, GAO Linghang. Simulation of Reinforcement Learning-based UAV Swarm Adversarial Strategy Deduction [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S2): 126-134. |
| [4] | LI Song, MA Zhuangzhuang, ZHANG Yunlin, SHAO Jinliang. Multi-agent Coverage Path Planning Based on Security Reinforcement Learning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S2): 101-113. |
| [5] | XU Peng, XING Boyang, LIU Yufei, LI Yongyao, ZENG Yi, ZHENG Dongdong. Anti-disturbance Composite Controller Design of Quadruped Robot Based on Extended State Observer and Model Predictive Control Technique [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S2): 12-21. |
| [6] | YANG Jiaxiu, LI Xinkai, ZHANG Hongli, WANG Hao. Robust Tracking of Quadrotor UAVs Based on Integral Reinforcement Learning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(9): 2802-2813. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jiandong, WANG Dinghan, YANG Qiming, SHI Guoqing, LU Yi, ZHANG Yaozhong. Multi-Dimensional Decision-Making for UAV Air Combat Based on Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(6): 1547-1563. |
| [8] | LI Chao, WANG Ruixing, HUANG Jianzhong, JIANG Feilong, WEI Xuemei, SUN Yanxin. Autonomous Decision-making and Intelligent Collaboration of UAV Swarms Based on Reinforcement Learning with Sparse Rewards [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(6): 1537-1546. |
| [9] | ZHENG Zexin, LI Wei, ZOU Kun, LI Yanfu. Anti-jamming Waveform Design of Ground-based Air Surveillance Radar Based on Reinforcement Learning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(5): 1422-1430. |
| [10] | LI Jiajian, SHI Yanjun, YANG Yu, LI Bo, ZHAO Xijun. Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning-based Offloading Decision for UAV Cluster Combat Tasks [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(11): 3295-3309. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yuanbo, XIANG Changle, WANG Weida, CHEN Yongdan. A Particle Swarm Optimization and Ant Colony Optimization Fusion Algorithm-based Model Predictve Torque Coordnation Control Strategy for Distributed Electric Drive Vehicle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(11): 3253-3258. |
| [12] | ZHAO Wenfei, CHEN Jian, WANG Yan, TENG Kenan. Dynamic Firepower Allocation for Cooperative Air Defense of Strategic Locations on the Sea Based on Reinforcement Learning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(11): 3516-3528. |
| [13] | TANG Zeyue, LIU Haiou, XUE Mingxuan, CHEN Huiyan, GONG Xiaojie, TAO Junfeng. Trajectory Tracking Control of Dual Independent Electric Drive Unmanned Tracked Vehicle Based on MPC-MFAC [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(1): 129-139. |
| [14] | SONG Jiarui, TAO Gang, LI Derun, ZANG Zheng, WU Shaobin, GONG Jianwei. Robust Model Predictive Control for Manned and Unmanned Vehicle Formation Based on Parameter Self-Optimization [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(1): 84-97. |
| [15] | ZHOU Qiu, ZHOU Yue, SUN Hongming, GUO Wei, WU Kai, LAN Yanjun. Path Planning and Tracking Control Method of Deep-Sea Landing Vehicle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(1): 298-306. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||