


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (9): 241051-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.1051
Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Zhenqing1, LIU Yan1,2,3,*( ), WANG Xiaofeng1, YAN Junbo1, BAI Fan1, SI Peng1,3, HUANG Fenglei1
), WANG Xiaofeng1, YAN Junbo1, BAI Fan1, SI Peng1,3, HUANG Fenglei1
Received:2024-11-19
Online:2025-09-24
Contact:
LIU Yan
CLC Number:
SHI Zhenqing, LIU Yan, WANG Xiaofeng, YAN Junbo, BAI Fan, SI Peng, HUANG Fenglei. Ballistic Characteristics of Quasi-elliptical Cross-section Projectile Penetrating into Finite-thick Concrete Target[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(9): 241051-.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| κ | a/mm | b/mm | l/mm | L/mm | m/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 14.0 | 46.7 | 33 |
Table 1 Geometric parameters of test projectile
| κ | a/mm | b/mm | l/mm | L/mm | m/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 14.0 | 46.7 | 33 |
| 实验 | 弹体质量 损失率/% | 靶板厚 度/mm | 时刻/ μs | v/ (m·s-1) | β/ (°) | α/ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.22 | 90 | 0 | 1053 | 2.34 | 0.81 |
| 346 | 812 | 4.41 | 4.95 | |||
| 423 | 805 | 4.41 | 5.92 | |||
| 500 | 802 | 4.41 | 6.88 | |||
| 2 | 2.50 | 90 | 0 | 1002 | 29.59 | 0.98 |
| 346 | 729 | 27.66 | -2.56 | |||
| 423 | 726 | 27.66 | -4.41 | |||
| 500 | 724 | 27.66 | -6.26 | |||
| 3 | 3.02 | 135 | 0 | 1006 | 0.79 | 0.73 |
| 500 | 658 | 9.2 | 1.02 | |||
| 616 | 658 | 9.2 | 1.21 | |||
| 732 | 658 | 9.2 | 1.87 | |||
| 4 | — | 135 | 0 | 1004 | 14.46 | 1.31 |
| 500 | 470 | 13.05 | -5.39 | |||
| 616 | 470 | 13.05 | -6.87 | |||
| 732 | 470 | 13.05 | -8.35 |
Table 2 Test conditions and results
| 实验 | 弹体质量 损失率/% | 靶板厚 度/mm | 时刻/ μs | v/ (m·s-1) | β/ (°) | α/ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.22 | 90 | 0 | 1053 | 2.34 | 0.81 |
| 346 | 812 | 4.41 | 4.95 | |||
| 423 | 805 | 4.41 | 5.92 | |||
| 500 | 802 | 4.41 | 6.88 | |||
| 2 | 2.50 | 90 | 0 | 1002 | 29.59 | 0.98 |
| 346 | 729 | 27.66 | -2.56 | |||
| 423 | 726 | 27.66 | -4.41 | |||
| 500 | 724 | 27.66 | -6.26 | |||
| 3 | 3.02 | 135 | 0 | 1006 | 0.79 | 0.73 |
| 500 | 658 | 9.2 | 1.02 | |||
| 616 | 658 | 9.2 | 1.21 | |||
| 732 | 658 | 9.2 | 1.87 | |||
| 4 | — | 135 | 0 | 1004 | 14.46 | 1.31 |
| 500 | 470 | 13.05 | -5.39 | |||
| 616 | 470 | 13.05 | -6.87 | |||
| 732 | 470 | 13.05 | -8.35 |
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | E/MPa | ν |
|---|---|---|
| 7.8 | 211 | 0.33 |
Table 3 Material parameters of projectile
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | E/MPa | ν |
|---|---|---|
| 7.8 | 211 | 0.33 |
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | 2.203 | λ1 | 0 | η1 | 0 |
| ν | 0.19 | λ2 | 8.000×10-6 | η2 | 0.85 |
| ft/MPa | 3.782 | λ3 | 2.400×10-5 | η3 | 0.97 |
| sLambda | 100 | λ4 | 4.000×10-5 | η4 | 0.99 |
| a0/MPa | 1.318×101 | λ5 | 5.600×10-5 | η5 | 1.00 |
| a1 | 4.463×10-1 | λ6 | 7.200×10-5 | η6 | 0.99 |
| a2/MPa-1 | 1.812×10-3 | λ7 | 8.800×10-5 | η7 | 0.97 |
| a0y/MPa | 9.955 | λ8 | 3.200×10-4 | η8 | 0.50 |
| a1y | 6.250×10-1 | λ9 | 5.200×10-4 | η9 | 0.10 |
| a2y/MPa-1 | 5.774×10-3 | λ10 | 5.700×10-4 | η10 | 0 |
| a1f | 4.41×10-1 | λ11 | 1.000 | η11 | 0 |
| a2f/MPa-1 | 2.652×10-3 | λ12 | 1.000×101 | η12 | 0 |
| omega | 0.5 | λ13 | 1.000×1010 | η13 | 0 |
| b3 | 0.0 | b1 | 1.0 | b2 | 5.0 |
| locwidth/cm | 1.2 | mxeps | 0.1 | fs | 1.967 |
Table 4 Material parameters of target
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ/(g·cm-3) | 2.203 | λ1 | 0 | η1 | 0 |
| ν | 0.19 | λ2 | 8.000×10-6 | η2 | 0.85 |
| ft/MPa | 3.782 | λ3 | 2.400×10-5 | η3 | 0.97 |
| sLambda | 100 | λ4 | 4.000×10-5 | η4 | 0.99 |
| a0/MPa | 1.318×101 | λ5 | 5.600×10-5 | η5 | 1.00 |
| a1 | 4.463×10-1 | λ6 | 7.200×10-5 | η6 | 0.99 |
| a2/MPa-1 | 1.812×10-3 | λ7 | 8.800×10-5 | η7 | 0.97 |
| a0y/MPa | 9.955 | λ8 | 3.200×10-4 | η8 | 0.50 |
| a1y | 6.250×10-1 | λ9 | 5.200×10-4 | η9 | 0.10 |
| a2y/MPa-1 | 5.774×10-3 | λ10 | 5.700×10-4 | η10 | 0 |
| a1f | 4.41×10-1 | λ11 | 1.000 | η11 | 0 |
| a2f/MPa-1 | 2.652×10-3 | λ12 | 1.000×101 | η12 | 0 |
| omega | 0.5 | λ13 | 1.000×1010 | η13 | 0 |
| b3 | 0.0 | b1 | 1.0 | b2 | 5.0 |
| locwidth/cm | 1.2 | mxeps | 0.1 | fs | 1.967 |
| 实验 | 剩余速度/(m·s-1) | 弹道偏转角/(°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验值 | 数值模 拟值 | 相对误 差/% | 实验值 | 数值模 拟值 | 相对误 差/% | |
| 1 | 802.3 | 773.9 | -3.5 | 2.068 | 2.095 | 1.31 |
| 2 | 723.5 | 704.6 | -2.6 | 1.930 | 1.754 | -9.13 |
| 3 | 658.0 | 632.4 | -3.9 | 9.987 | 10.330 | 3.44 |
| 4 | 470.3 | 462.4 | -1.7 | 1.416 | 1.085 | -23.42 |
Table 5 Comparison of test and simulated results
| 实验 | 剩余速度/(m·s-1) | 弹道偏转角/(°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实验值 | 数值模 拟值 | 相对误 差/% | 实验值 | 数值模 拟值 | 相对误 差/% | |
| 1 | 802.3 | 773.9 | -3.5 | 2.068 | 2.095 | 1.31 |
| 2 | 723.5 | 704.6 | -2.6 | 1.930 | 1.754 | -9.13 |
| 3 | 658.0 | 632.4 | -3.9 | 9.987 | 10.330 | 3.44 |
| 4 | 470.3 | 462.4 | -1.7 | 1.416 | 1.085 | -23.42 |
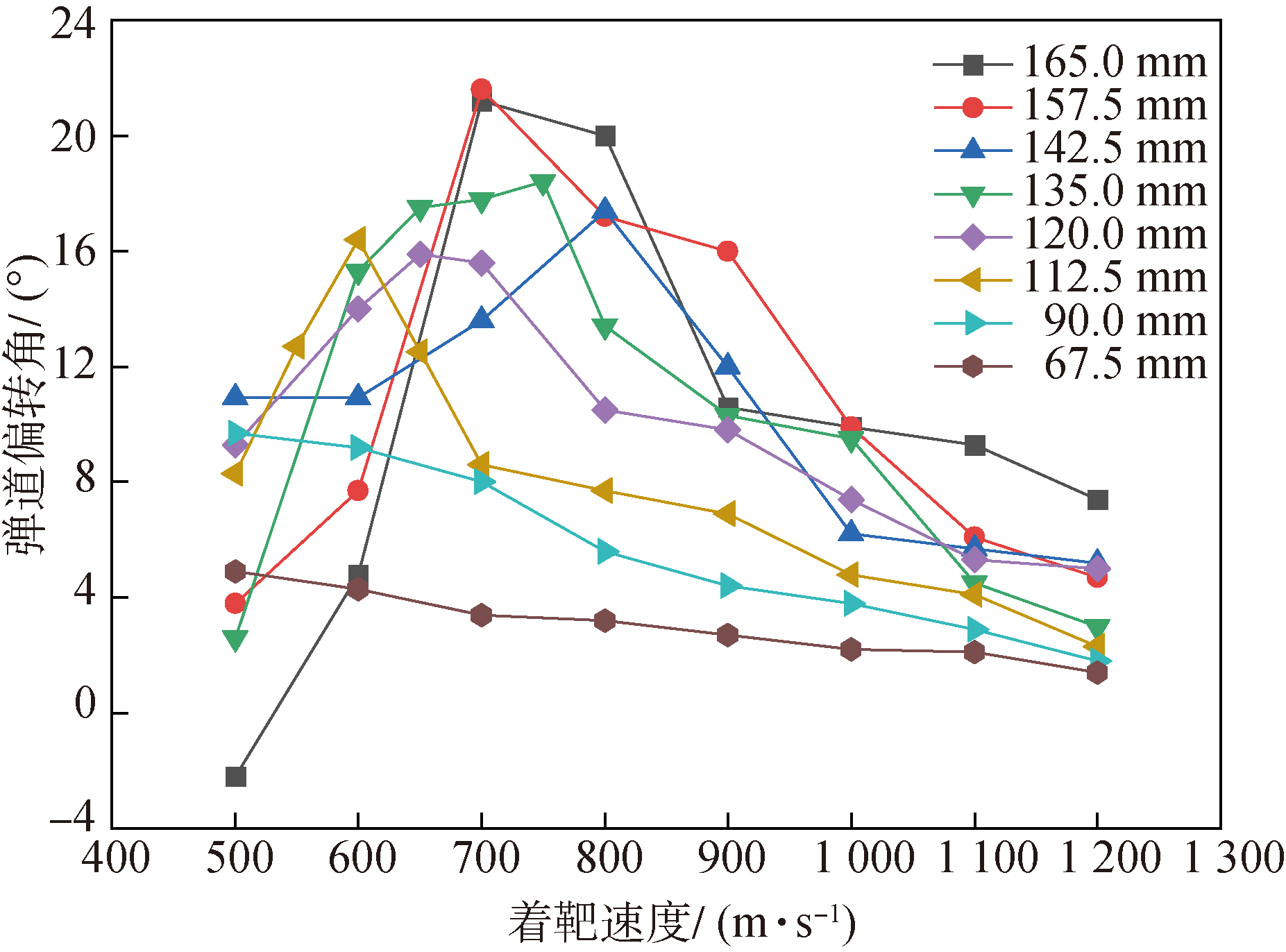
Fig.17 The trajectory deflection angles of projectiles penetrating into the target plates with different thicknesses at different normal penetration velocities
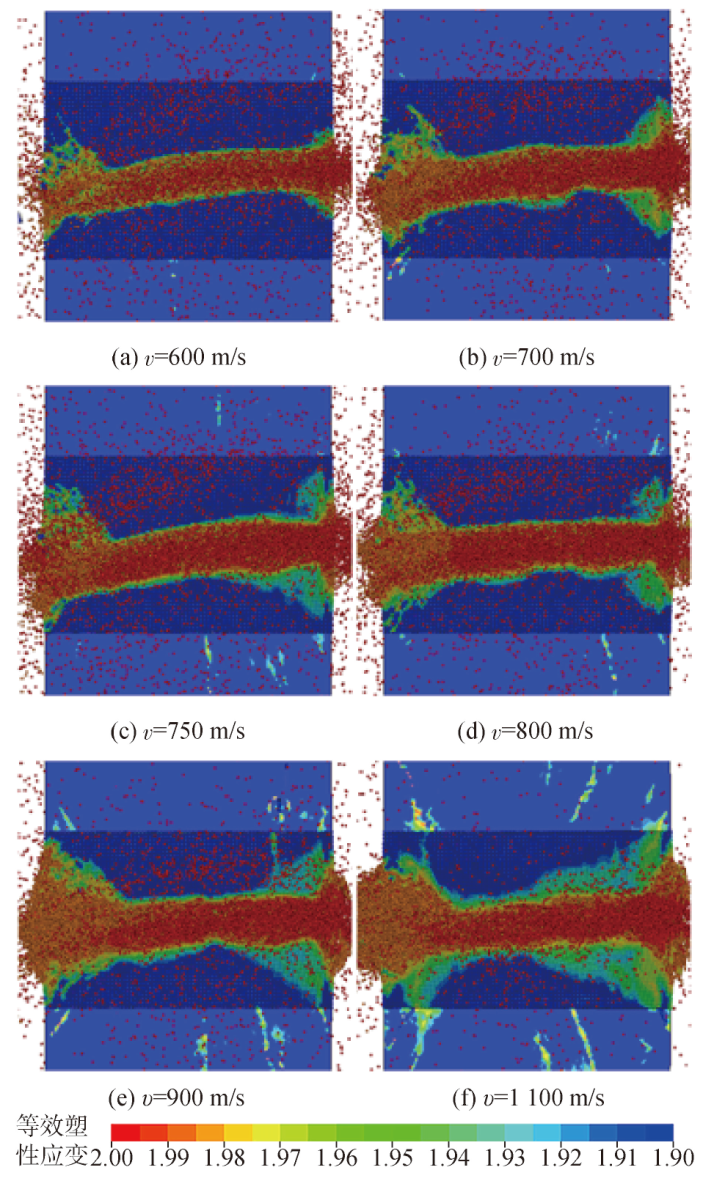
Fig.18 The equivalent plastic strain contours within the 135mm- thick target plate during normal penetration by a projectile at typical impact velocities
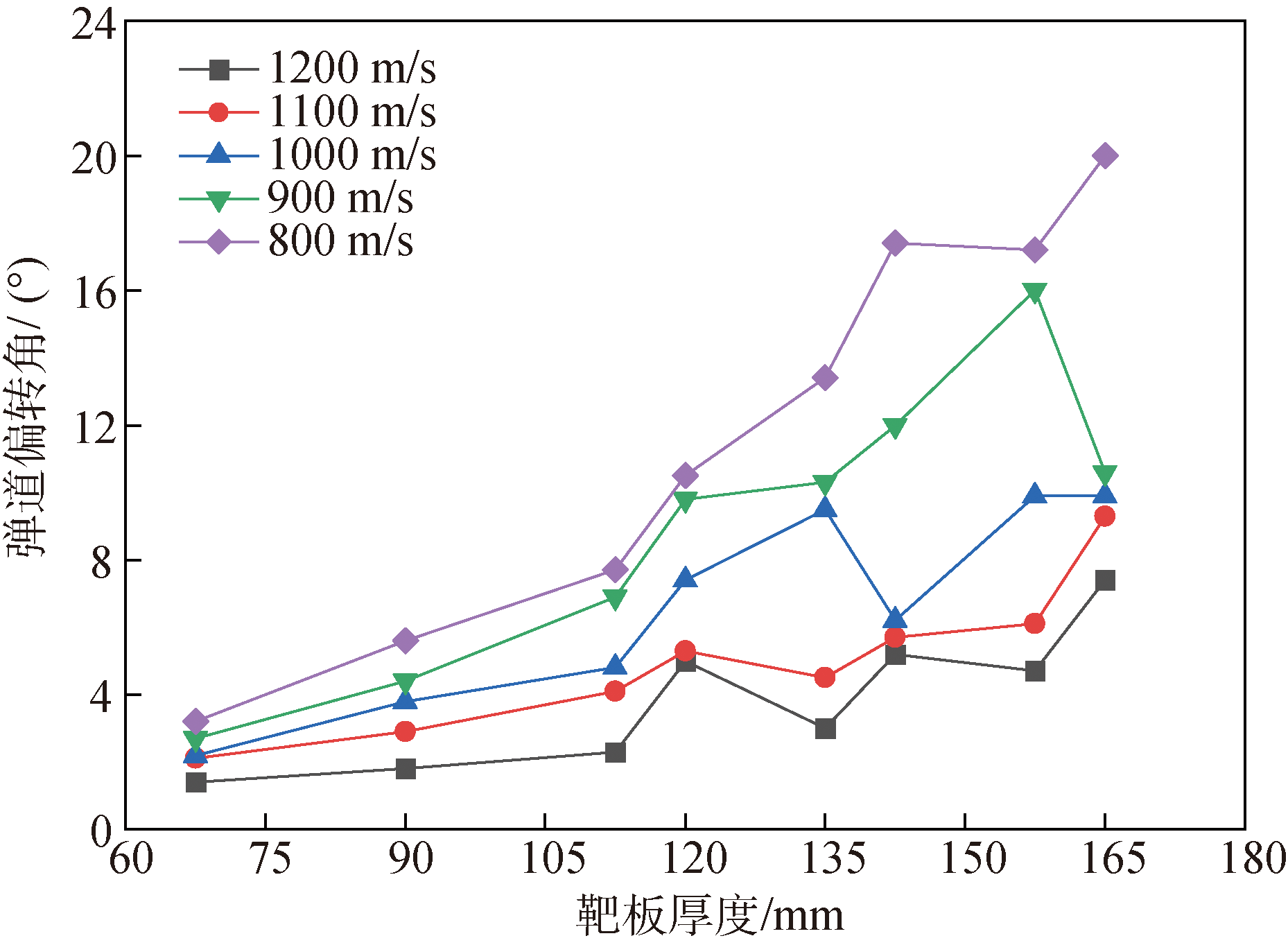
Fig.20 The trajectory deflection angles of projectiles penetrating into the targets with different thicknesses under normal penetration at same impact velocity
| [1] |
董恒, 黄风雷, 武海军, 等. 异形弹体高速侵彻/穿甲机理研究进展[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(9):2863-2887.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0040 |
|
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0040 |
|
| [2] |
邓希旻, 武海军, 董恒, 等. 椭圆截面截锥弹体的高速穿甲特性及阻力模型[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9):104-120.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
田泽, 王浩, 武海军, 等. 椭圆变截面弹体斜贯穿薄靶姿态偏转机理[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(7):1537-1552.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0367 |
|
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0367 |
|
| [4] |
蒋腾, 武海军, 邓希旻, 等. 变截面弹体斜侵彻两层间隔钢靶弹道特性[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(2):240019.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0019 |
|
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0019 |
|
| [5] |
魏海洋, 张先锋, 熊玮, 等. 椭圆截面弹体斜侵彻金属靶体弹道研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(2):90-102.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
王文杰, 张先锋, 邓佳杰, 等. 椭圆截面弹体侵彻砂浆靶规律分析[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(1):164-173.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
岳胜哲, 陈利, 张晓伟, 等. 非对称类椭圆截面弹体斜贯穿铝靶数值模拟研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(4):127-133.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
王景琛, 张晓伟, 张庆明, 等. 非圆截面弹体斜侵彻薄靶的动态载荷特性研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2023, 44(1):127-135.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
朱超, 张晓伟, 张庆明, 等. 弹体斜侵彻双层钢板的结构响应和失效研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9):091408.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
王皓, 高旭东. 类椭圆截面战斗部侵彻混凝土弹道特性研究[J]. 兵工自动化, 2020, 39(5):68-72.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
董恒. 椭圆截面弹体侵彻混凝土靶作用过程与结构响应研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2021.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
杨士林, 高旭东, 张先锋, 等. 椭圆类截面弹体侵彻多层间隔钢靶的弹道特性[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2025, 45(3):033303.
|
|
|
| [1] | LIU Gentong, JIANG Yi, CAI Yunlong. Oblique Cold Launch Technology of Mars Ascent Vehicle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(8): 240957-. |
| [2] | WANG Meng, LIN Wenqi, CUI Qingchun, HAN Xuanxuan. A Multi-gunpowder Adaptive Tailstock Forward-throwing Technology Based on Pressure Difference Separation [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(7): 240752-. |
| [3] | HOU Yunkun, TANG Kui, WANG Jinxiang, GU Minhui, HAO Xulong, WANG Jirui. Characteristics of Oblique Penetration of Metal Targets by Jacketed Rods with Different Noses [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(4): 240417-. |
| [4] | LIU Pengzhan, WANG Guoqiang, JING Chunwen, ZHAO Xiongfei, LIU Wanchuan, WANG Yong. Research on Interior Ballistics Stability of Small-caliber Recoilless Gun with High Muzzle Velocity of Projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(4): 240245-. |
| [5] | JIANG Teng, WU Haijun, DENG Ximin, QUAN Xin, DONG Heng, HUANG Fenglei. Study on Ballistic Characteristics of Variable Cross-section Projectile Obliquely Penetrating Two-layer Spacer Steel Target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(2): 240019-. |
| [6] | GUO Junting, YU Yonggang. Complex Flow Field Characteristics inside Combustion Chamber During the Secondary Ignition Process of CTA [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(7): 2282-2293. |
| [7] | PEI Guiyan, NIE Jianxin, WANG Qiushi, JIAO Qingjie, DU Zhipeng, LI Ying. Study on Oblique Penetration of Metal Plate by Naval Gun Semi-armor-piercing Simulation Projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(3): 731-743. |
| [8] | LOU Wenzhong, HE Bo, YUAN Yong, LI Zhipeng, SHAN Liang, FENG Hengzhen, ZHANG Mingrong, ZHU Haokun. An Equivalent Simulation Test System for Complex Terminal Ballistics of Fuze Based on Counter Target Method [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(12): 4554-4564. |
| [9] | CHEN Baihan, SHEN Zikai, ZOU Huihui, WANG Weiguang, WANG Kehui. Basic Evolution Characteristics of Oblique Penetration of Projectile against Hard Target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S1): 59-66. |
| [10] | LIU Hongfu, HUANG Fenglei, BAI Zhiling, DUAN Zhuoping. Theoretical Model of Oblique Penetration of Rigid Projectiles into Concrete Targets at Attack Angles [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(8): 2381-2390. |
| [11] | TIAN Zhongliang, LI Junwei, HE Ye, XU Tuanwei, DING Miao, WANG Ningfei. Analysis of Interior Ballistic Characteristics of Conical Three-Dimensional Charge Column Under Lateral Overload [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(7): 1896-1907. |
| [12] | WANG Xueqin, MA Wuning, MA Dawei, WANG Shanglong, ZHANG Zhendong. Accurate Internal Ballistics Modeling and Testing of Rodless High Pressure Pneumatic Catapult Considering Leakage [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(7): 1867-1880. |
| [13] | ZHAO Zixi, JIANG Yi, JIA Qiming, NIU Yusen. Research on Interior Ballistics of Catapult using High-Pressure working medium [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(7): 1553-1564. |
| [14] | ZENG Peigao, JIANG Yi, YANG Lina. Interior Ballistics of Independent Water-surface Launching Canister [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(6): 1266-1276. |
| [15] | WANG Jingcheng, LI Xiaogang, YE Yaokun, DING Feng, XIONG Shihui, WEN Yuquan. Model Formulation and Influencing Factors for a Separation Nut Considering the Combustion of Multiple Pyrotechnic Charges [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(12): 3070-3081. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||