


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 2712-2727.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0616
Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Zhengping, YANG Guolai*( ), LI Lei**(
), LI Lei**( ), WANG Liqun
), WANG Liqun
Received:2023-06-28
Online:2023-09-24
Contact:
YANG Guolai, LI Lei
CLC Number:
SUN Zhengping, YANG Guolai, LI Lei, WANG Liqun. Thermal Demagnetization Characteristics of Nd-Fe-B Used in Eddy Current Recoil Mechanism of Artillery[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(8): 2712-2727.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 晶相 | Ms/(A·m-1) | K1/(J·m-3) | Ae/(J·m-1) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主相 | 1.28×106 | 4.2×106 | 1.047×10-11 | 0.010 |
| 界相 | 1.28×103 | 4.2×104 | 1.047×10-12 | 0.002 |
Table 1 Magnetic parameters of Nd-Fe-B
| 晶相 | Ms/(A·m-1) | K1/(J·m-3) | Ae/(J·m-1) | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主相 | 1.28×106 | 4.2×106 | 1.047×10-11 | 0.010 |
| 界相 | 1.28×103 | 4.2×104 | 1.047×10-12 | 0.002 |
| 温度/ ℃ | 饱和磁 化强度/ (kA·m-1) | 畴间耦 合参数/ (kA·m-1) | 形状 参数 | 钉扎 损耗/ (kA·m-1) | 可逆 磁化率 | 拟合 精度/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1300 | 102 | 0.840 | 1310 | 0.0002 | 93.1 |
| 40 | 1280 | 104 | 0.735 | 1105 | 0.0002 | 92.4 |
| 60 | 1250 | 111 | 0.631 | 848 | 0.0002 | 82.5 |
| 80 | 1240 | 97 | 0.549 | 655 | 0.0002 | 82.1 |
| 100 | 1220 | 99 | 0.453 | 480 | 0.0002 | 79.2 |
Table 2 Parameter values of J-A model at different temperatures
| 温度/ ℃ | 饱和磁 化强度/ (kA·m-1) | 畴间耦 合参数/ (kA·m-1) | 形状 参数 | 钉扎 损耗/ (kA·m-1) | 可逆 磁化率 | 拟合 精度/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1300 | 102 | 0.840 | 1310 | 0.0002 | 93.1 |
| 40 | 1280 | 104 | 0.735 | 1105 | 0.0002 | 92.4 |
| 60 | 1250 | 111 | 0.631 | 848 | 0.0002 | 82.5 |
| 80 | 1240 | 97 | 0.549 | 655 | 0.0002 | 82.1 |
| 100 | 1220 | 99 | 0.453 | 480 | 0.0002 | 79.2 |
| 材料 | 电导率/(S·m-1) | 相对介电常数 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 恒压热容/(J·kg-1·℃-1) | 导热率/(W·m-1·℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 (内筒材料) | 2.7×107 | 1 | 3900 | 900 | 238 |
| DT4 (外筒材料) | 2.0×107 | 1 | 7860 | 460 | 46 |
| 空气 | 1 | 1 | 1.293 | 1004 | 0.0244 |
Table 3 Material parameters of alumina, DT4 and air
| 材料 | 电导率/(S·m-1) | 相对介电常数 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 恒压热容/(J·kg-1·℃-1) | 导热率/(W·m-1·℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 (内筒材料) | 2.7×107 | 1 | 3900 | 900 | 238 |
| DT4 (外筒材料) | 2.0×107 | 1 | 7860 | 460 | 46 |
| 空气 | 1 | 1 | 1.293 | 1004 | 0.0244 |
| 电导率/(S·m-1) | 相对介电常数 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 恒压热容/(J·kg-1·℃-1) | 导热率/(W·m-1·℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.25×105 | 1 | 7400 | 400 | 8.95 |
Table 4 Nd-Fe-B basic material parameters
| 电导率/(S·m-1) | 相对介电常数 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 恒压热容/(J·kg-1·℃-1) | 导热率/(W·m-1·℃-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.25×105 | 1 | 7400 | 400 | 8.95 |
| Ms/(kA·m-1) | αja/(kA·m-1) | a | k/(kA·m-1) | c | 初始磁化强度/(kA·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -T+1318 | -0.00483T+0.93 | -10.45T+1503 | 102 | 0.0002 | -1.066T+1172 |
Table 5 Magnetic parameters of Nd-Fe-B under J-A hysteresis model
| Ms/(kA·m-1) | αja/(kA·m-1) | a | k/(kA·m-1) | c | 初始磁化强度/(kA·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -T+1318 | -0.00483T+0.93 | -10.45T+1503 | 102 | 0.0002 | -1.066T+1172 |
| 剩磁/T | 真空磁导率/(H·m-1) | 相对磁导率 |
|---|---|---|
| -0.00134T+1.4727 | 4π×107 | e0.0108T |
Table 6 Magnetic parameters of Nd-Fe-B under the residual flux density model
| 剩磁/T | 真空磁导率/(H·m-1) | 相对磁导率 |
|---|---|---|
| -0.00134T+1.4727 | 4π×107 | e0.0108T |
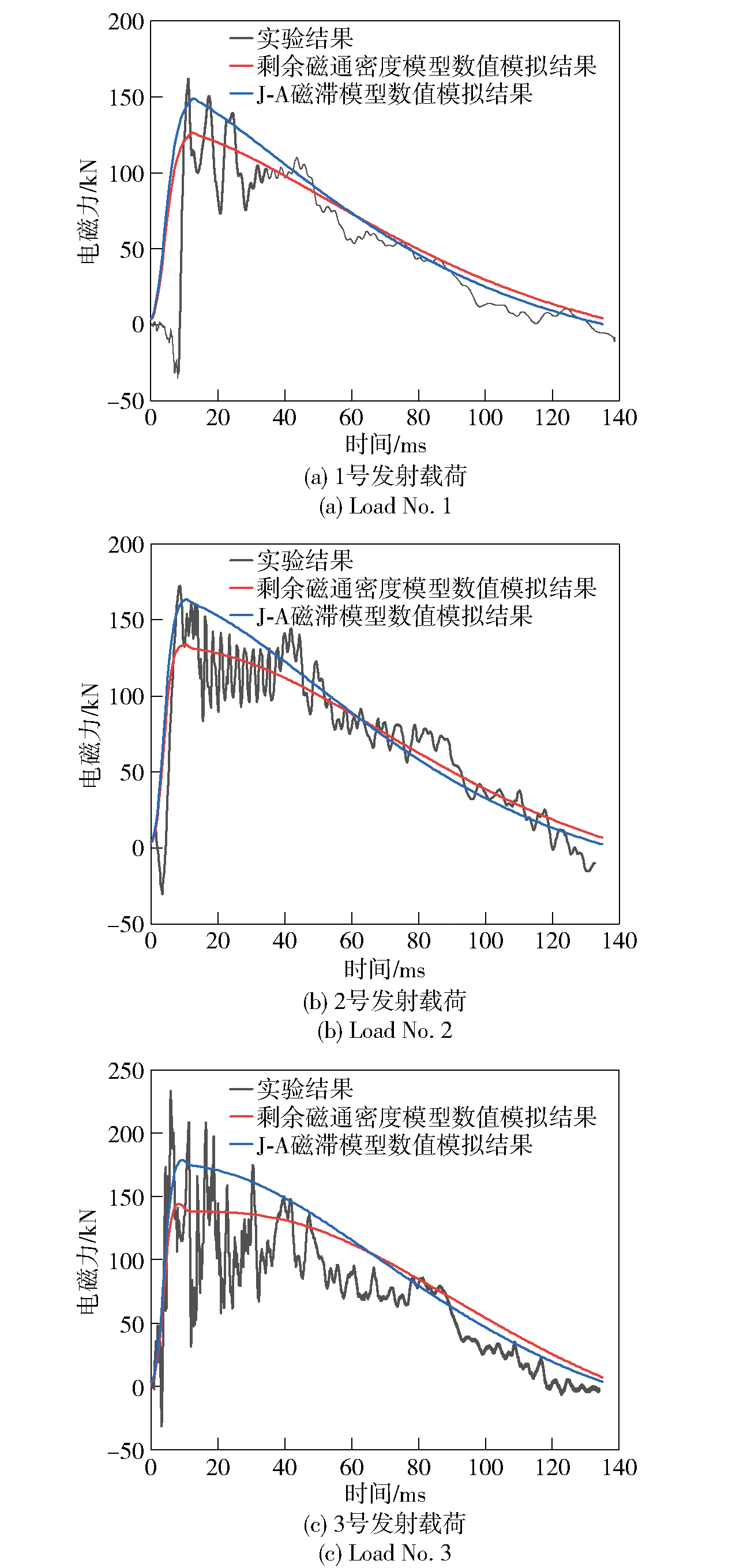
Fig.14 Comparison of electromagnetic braking forces in the impact experiment of prototype, and the numerical simulations of residual magnetic flux density model and J-A hysteresis model
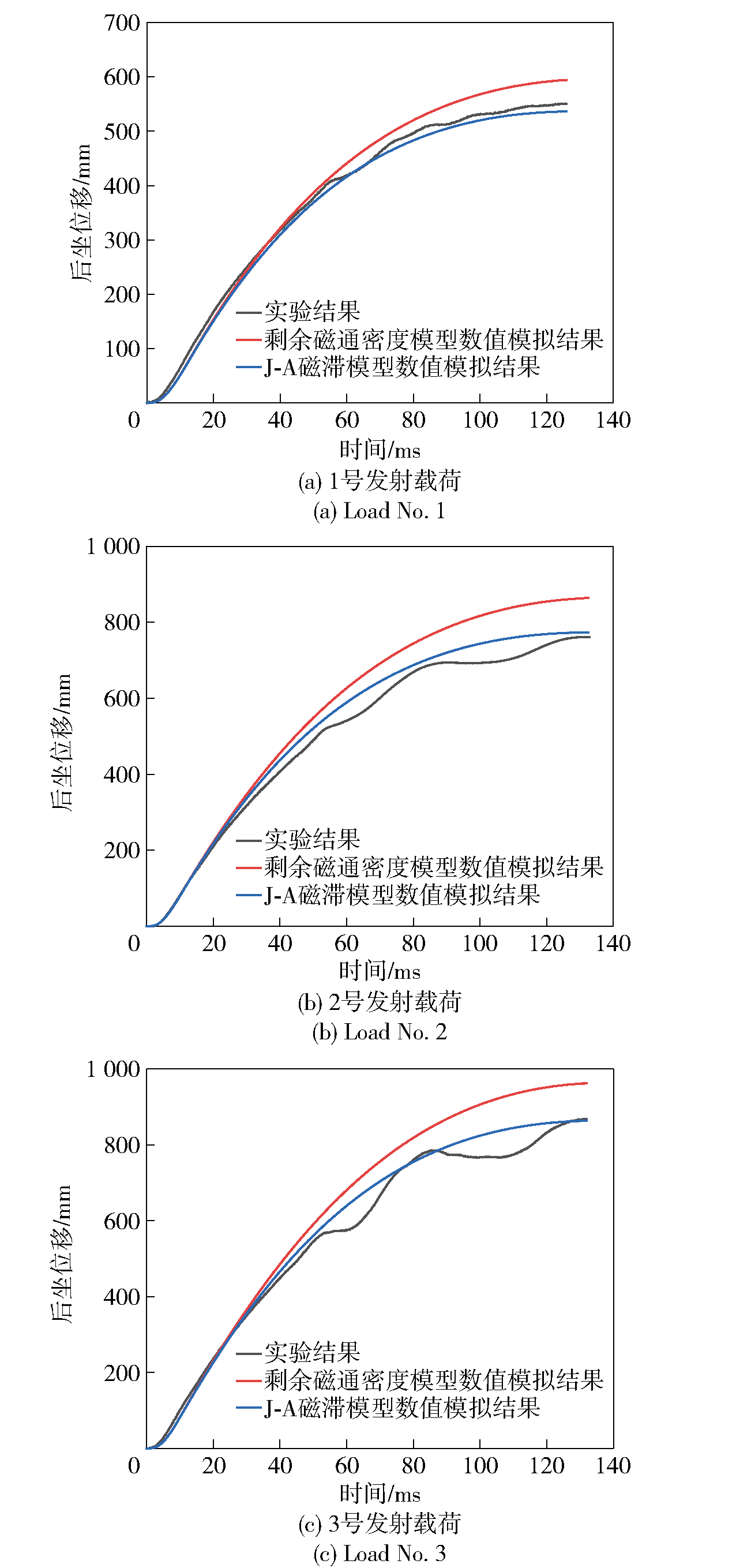
Fig.15 Comparison of recoil displacements in the impact test of prototype, and the numerical simulations of residual magnetic flux density model and J-Ahysteresis model
| 工况 | 原理样机 实验结果 | 剩余磁 通模型 | J-A模型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 550 | 594(44) | 536(-14) |
| 2 | 761 | 864(103) | 773(12) |
| 3 | 867 | 962(95) | 863(-4) |
Table 7 Maximum recoil displacementmm
| 工况 | 原理样机 实验结果 | 剩余磁 通模型 | J-A模型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 550 | 594(44) | 536(-14) |
| 2 | 761 | 864(103) | 773(12) |
| 3 | 867 | 962(95) | 863(-4) |
| 工况 | 温度 | 最大去磁量/T | 最大后坐位移/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.044 | 536 | |
| 1 | 40 | 0.082 | 549 |
| 60 | 0.155 | 570 | |
| 80 | 0.257 | 628 | |
| 20 | 0.052 | 773 | |
| 2 | 40 | 0.094 | 796 |
| 60 | 0.176 | 848 | |
| 80 | 0.317 | 919 | |
| 20 | 0.056 | 863 | |
| 3 | 40 | 0.095 | 912 |
| 60 | 0.179 | 986 | |
| 80 | 0.351 | 1108 |
Table 8 Maximum demagnetization and maximum recoil displacement under different working conditions
| 工况 | 温度 | 最大去磁量/T | 最大后坐位移/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.044 | 536 | |
| 1 | 40 | 0.082 | 549 |
| 60 | 0.155 | 570 | |
| 80 | 0.257 | 628 | |
| 20 | 0.052 | 773 | |
| 2 | 40 | 0.094 | 796 |
| 60 | 0.176 | 848 | |
| 80 | 0.317 | 919 | |
| 20 | 0.056 | 863 | |
| 3 | 40 | 0.095 | 912 |
| 60 | 0.179 | 986 | |
| 80 | 0.351 | 1108 |
| [1] |
高跃飞. 火炮反后坐装置设计[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
张相炎. 新概念火炮技术[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014: 42-50.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
李子轩, 杨国来, 刘宁. 强冲击载荷下电磁缓冲器有限元仿真模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(5): 913-923.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.05.003 |
|
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.05.003 |
|
| [4] |
李子轩, 杨国来, 孙全兆, 等. 强冲击载荷下永磁式电涡流阻尼器阻力特性及优化研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(4): 664-671.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.04.005 |
|
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
吴波, 邓小霞. 新能源汽车驱动电机用烧结钕铁硼磁体的热稳定性[J]. 磁性材料及器件, 2019, 50(3): 51-54, 72.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
姜寿亭, 李卫. 凝聚态磁性物理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
李雷. 强冲击环境下电涡流制退机用烧结钕铁硼的力磁特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2022.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
余伟超. 基于磁结构的自旋波动力学[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2018.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [1] | HAN Jiaxiang, BAI Qiaodong, QIU Han, ZHENG Quan, WENG Chunsheng. Influence of Combustor Configuration on Rotating Detonation Characteristics of Kerosene Pre-combustion Cracking Gas [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(8): 2837-2850. |
| [2] | JIANG Xinli, ZHANG Guokai, HE Yong, YAO Jian, WANG Zhen, WU Yuxin, LIU Ju, WANG Mingyang. Afterburning Effect of Thermobaric Explosives in Confined Space [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(8): 2520-2530. |
| [3] | GUO Junting, YU Yonggang. Complex Flow Field Characteristics inside Combustion Chamber During the Secondary Ignition Process of CTA [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(7): 2282-2293. |
| [4] | WANG Cheng, WANG Weiguo, MENG Chen, LI Qing, CHENG Yue, KONG Zihua. Simulation of Four-element Infrared Detection System Considering Missile Spinning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(7): 2218-2227. |
| [5] | ZUO Mingshuo, XU Yuxin, LI Yongpeng, LI Xudong, GUO Delong, YANG Xiang. Dynamic Response of Directional Blast Relief Container Structure for Civil Aircraft under Internal Explosive Loading [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(7): 2383-2392. |
| [6] | ZHAO Wei, HOU Baolin, YAN Shaojun, BAO Dan, LIN Yubin. A Dynamic Model of Interval Uncertainty of Rotational Chain Shell Magazine [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(6): 1991-2002. |
| [7] | DING Wei, MING Zhenjun, WANG Guoxin, YAN Yan, YU Lei. Optimization Design Method of Complex Equipment System-of-systems Based on Forward Analytical Formula and MOGT Optimization Algorithm [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(6): 1974-1990. |
| [8] | YANG Jin, HAO Xinhong, QAO Caixia, CHEN Qile. Research on Anti-frequency Sweeping Jamming Method for Frequency-modulated Fuze Based on Sparse Recovery [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(6): 2044-2053. |
| [9] | LI Yanze, QIAN Linfang, FU Jiawei, CHEN Longmiao. Study on the Equivalent Full Charge Conversion Coefficient of the Barrel Life Based on the Thermal-chemical Erosion Model [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(5): 1426-1435. |
| [10] | SHI Junfei, QIAN Linfang, CHEN Guangsong, YIN Qiang, LIU Daokun, LI Zhonggang. Research on the Procedural Burning Characteristics of Cased Telescoped Ammunition Based on Digital Image Correlation Principle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(4): 1047-1059. |
| [11] | CHEN Baihan, ZHAO Shengwei, ZOU Huihui, WANG Weiguang, DAI Xianghui, WANG Kehui. Research Progress of Overload Signal Characteristics and Processing Technologies of Penetrating Projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 0, (): 0-0. |
| [12] | YAN Qingdong, ZHU Ming, WEI Wei, LIU Cheng, WANG Meiwei. Analysis of Contact Dynamics Characteristics of Tire-snow Interaction in Semi-infinite Snow Region [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(3): 925-933. |
| [13] | LIU Ju, ZHANG Guokai, WANG Zhen, YAO Jian, LI Jie, YU Siyuan, JI Yuguo. Experimental Study on the Damage Characteristics and Laws of RC Beams under Close-in Blast Loading of Thermobaric Explosives [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(3): 864-874. |
| [14] | BAO Dan, WEI Yukai, JIN Xin, HOU Baolin. Adaptive Control of Magazines Considering Output Constraints and Input Saturation [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(3): 789-797. |
| [15] | WANG Liang, WANG Shoukun, Niu Tianwei, WANG Junzheng . Speed control method of unmanned special vehicle based on terrain feature time-frequency transform [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 0, (): 0-0. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||