


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1985-1992.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0228
Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Qiang1,2, CHEN Ling1,2, GAN Huaiyin1,2, ZHU Yongchen1,2, HE Weidong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-06
Online:2023-07-30
Contact:
HE Weidong
LI Qiang, CHEN Ling, GAN Huaiyin, ZHU Yongchen, HE Weidong. Electrostatic Spraying Preparation and Performance of Nanocomposite Energetic Material RDX@NGEC[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(7): 1985-1992.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
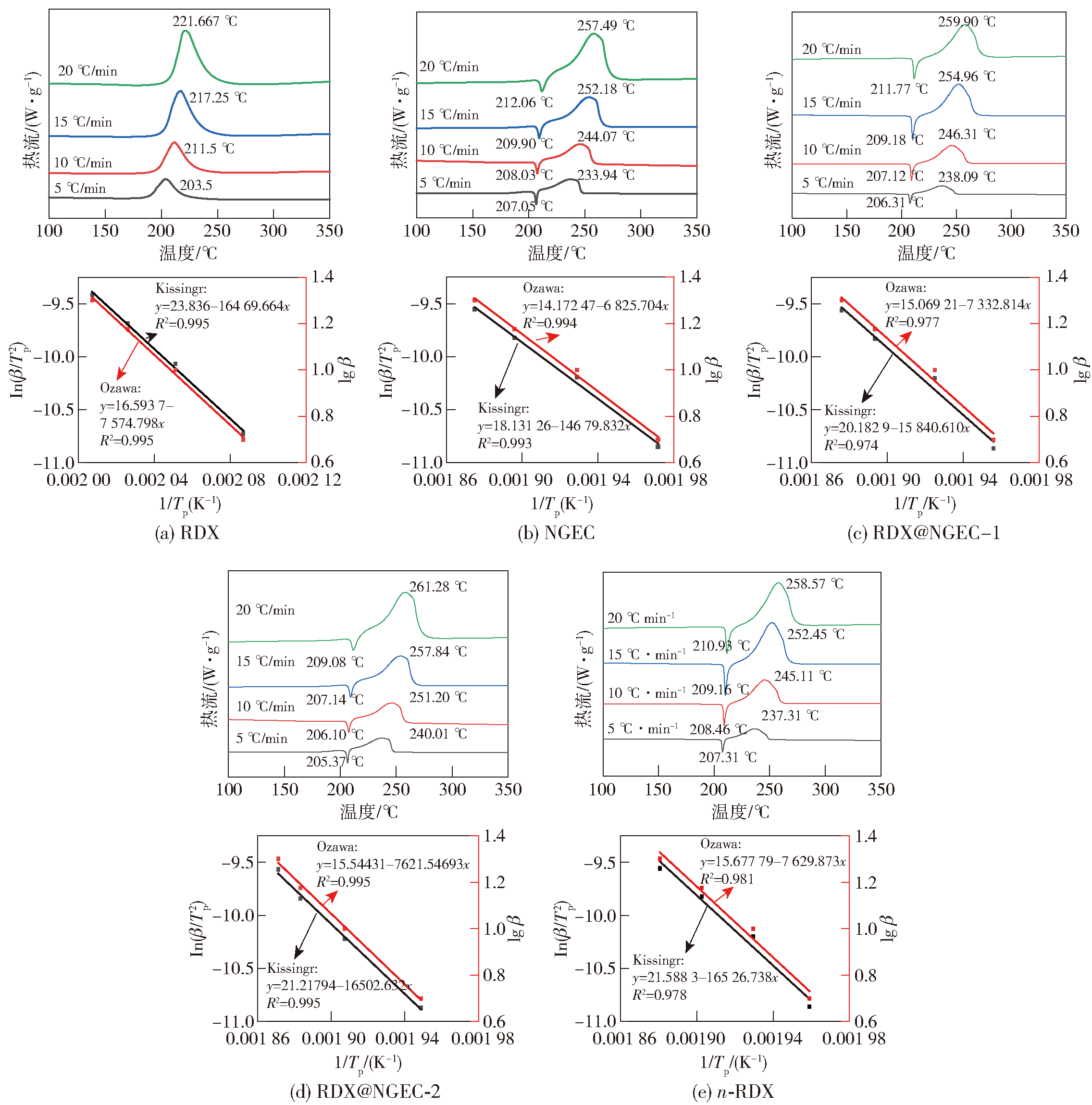
Fig.6 DSC trajectories (top) of NGEC, RDX, RDX@NGEC-1, RDX@NGEC-2 at different heating rates and the linearity of the thermodynamic calculations by Kissinger and Ozawa (bottom) methods, respectively Fitting graph
| 样品 | Tp/K | 热力学参数 | 动力学参数 | 热稳定性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔH≠/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG≠/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔS≠/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) Kissinger | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) Ozawa | lnAk | k | Tb/K | ||
| NGEC | 465.3 | 133.063 | 122.840 | 21.970 | 136.931 | 137.898 | 33.545 | 0.157 | 479.245 |
| RDX | 495.72 | 117.929 | 131.285 | -26.942 | 122.050 | 124.261 | 27.725 | 0.151 | 513.696 |
| n-RDX | 502.96 | 133.224 | 149.005 | -31.376 | 137.406 | 138.900 | 27.207 | 0.00351 | 519.276 |
| 1 | 507.59 | 127.481 | 149.556 | -43.490 | 131.701 | 133.493 | 25.759 | 0.00430 | 524.989 |
| 2 | 496.07 | 133.081 | 149.900 | -33.904 | 137.206 | 138.749 | 26.889 | 0.00170 | 511.952 |
Table 1 Thermodynamics, kinetics and thermal stability parameters
| 样品 | Tp/K | 热力学参数 | 动力学参数 | 热稳定性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔH≠/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG≠/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔS≠/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) Kissinger | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) Ozawa | lnAk | k | Tb/K | ||
| NGEC | 465.3 | 133.063 | 122.840 | 21.970 | 136.931 | 137.898 | 33.545 | 0.157 | 479.245 |
| RDX | 495.72 | 117.929 | 131.285 | -26.942 | 122.050 | 124.261 | 27.725 | 0.151 | 513.696 |
| n-RDX | 502.96 | 133.224 | 149.005 | -31.376 | 137.406 | 138.900 | 27.207 | 0.00351 | 519.276 |
| 1 | 507.59 | 127.481 | 149.556 | -43.490 | 131.701 | 133.493 | 25.759 | 0.00430 | 524.989 |
| 2 | 496.07 | 133.081 | 149.900 | -33.904 | 137.206 | 138.749 | 26.889 | 0.00170 | 511.952 |
| [1] |
王泽山, 何卫东, 徐复铭. 火药装药设计原理与技术[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2006.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
王泽山. 发射药技术的展望[J]. 华北工学院学报(社科版), 2001(增刊1): 34-40.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c00874 URL |
| [4] |
刘佳, 马忠亮, 张丽华, 等. 微观参量表征RDX含量对非均质单基发射药力学性能的影响[J]. 含能材料, 2015, 23(7): 676-681.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
邵自强. 硝化纤维素生产工艺及设备[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2002.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
夏勇, 梁昊, 何卫东. 纳米纤维素纤维在高能太根发射药中的应用[J]. 含能材料, 2018, 26(2): 118-122.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
徐坤, 邵自强, 王飞俊, 等. 纤维素基新型热塑性含能粘合剂中间体合成[J]. 含能材料, 2004, 4(2): 65-68.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
张有德, 邵自强, 李博, 等. NGEC的热行为和热分解机理[J]. 含能材料, 2010, 18(5):568-573.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
王飞俊, 杨斐霏, 王江宁, 等. NGEC基改性双基推进剂的制备及性能[J]. 火炸药学报, 2006, 4(6):51-53.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c03263 URL |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1039/C8RA04122A URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1007/s00396-015-3620-x URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1021/cg049965a URL |
| [18] |
doi: S0304-3894(16)30265-5 pmid: 27016668 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2014.04.002 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.12.005 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c03263 URL |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2017.05.002 URL |
| [26] |
张冬冬, 姚箭, 李斌. RDX基复合物静电喷雾法制备及性能研究[J]. 爆破器材, 2017, 46(5):18-22.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
晋苗苗, 罗运军. 硝化棉/黑索今纳米复合含能材料的制备与热性能研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(6): 822-827.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2014.06.011 |
|
|
|
| [29] |
石晓峰, 王晶禹, 李小东, 等. RDX基复合含能微球的制备及表征[J]. 含能材料, 2015, 23(5):428-432.
|
|
|
| [1] | XU Ruixuan, XU Jiaxing, XUE Zhihua, LÜ Jieyao, YAN Qilong. Preparation and Thermal Decomposition Properties of Multi-scale Interface-Tunable Al/RDX Energetic Composites [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(3): 691-701. |
| [2] | WAN Ziping, TAN Ruoyu, ZHENG Jieji, REN Guang'an, XIE Xin, FAN Dapeng. Efficient Design Method of Multi-condition and Static and Dynamic Reinforced Wall Structure for Modular Base of Weapon Station [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(2): 577-590. |
| [3] | LI Meng, WU Haijun, DONG Heng, REN Guang, ZHANG Peng, HUANG Fenglei. Machine Learning-based Models for Predicting the Penetration Depth of Concrete [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(12): 3771-3782. |
| [4] | WEI Wei, ZHANG Jingwen, CHANG Sijiang, WANG Haosheng, WANG Jianzhong. Global Sensitivity Analysis of Bullet's Angular Velocity Based on Sobol and EFAST Method [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(9): 2408-2416. |
| [5] | SHI Shuzheng, GENG Wenping, LIU Yong, BI Kaixi, LI Fen, CHOU Xiujian. Piezoelectric MEMS Accelerometer With d31 Mode Cantilever Structure [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(8): 1998-2006. |
| [6] | LI Lei, WANG Yanwei, DANG Li, WANG Huisi, DU Fang, TAO Bowen, HU Xiang, ZHOU Shuiping, GU Jian. Hygroscopic Properties of Ammonium Dinitroamide-based High Energy Propellant [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(7): 1614-1619. |
| [7] | WANG Fan, GUO Weiguo, WU Qian, GAO Meng. Calibration Method for Sensitivity Coefficient of High-temperature Strain Gauges at High Strain Rate [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(4): 899-909. |
| [8] | LIU Chang, WANG Jiang, FAN Shipeng, LI Ling, LIN Defu. BP Neural Network-Based Adaptive Biased Proportional Navigation Guidance Law [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(11): 2798-2809. |
| [9] | LIU Chun, OU Zhuocheng, DUAN Zhuoping, HUANG Fenglei. Hot Spot Temperature Resulting from Elliptical Void Collapse in PBX under Dynamic Loading and Its Semi-empirical Analytical Expression [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(1): 57-68. |
| [10] | DANG Quanyong, GE Yanxin, GAO Yubo. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Al2O3/SiC Composite Ceramic Subjected to Impact Loading [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(1): 175-180. |
| [11] | NING Zixuan, WANG Lin, CHENG Xingwang, CHENG Huanwu, LIU Anjin, XU Xuefeng, ZHOU Zhe, ZHANG Binbin. Dynamic Response Behaviors of Ti-6321 Titanium Alloys with Different Microstructures under Split Hopkinson Pressure BarLoading [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(4): 862-870. |
| [12] | LUO Zhongfeng, GUAN Xiaorong, XU Cheng. Global Sensitivity Analysis of a Self-propelled Gun's Structural Parameters for Position and Attitude of Projectile at Muzzle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(2): 254-267. |
| [13] | CHEN Pengfei, HE Peng, YU Tailong, LIU Qiaoling. An Analysis Method for Nonlinear Structural Reliability Based on Gradient Search Method [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(1): 175-184. |
| [14] | LIN Tong, QIAN Linfang, FU Jiawei, WANG Mingming. Parameter Identification and Sensitivity analysis of Gun Elevating Equilibrator [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(9): 1736-1744. |
| [15] | HOU Yufei, XU Jinsheng, ZHOU Changsheng, CHEN Xiong, LI Hongwen. Comparation of Solid Propellant Micromodels with and without Damage at Initial Particle/matrix Interface [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(9): 1800-1808. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||