


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1330-1338.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-01-05
Online:2022-07-05
Contact:
YU Yonggang
LI Ziyu, YU Yonggang. Analysis of Propellant Pellets’ Dispersion Characteristics of Single Modular Charge Based on Discrete Element Method for Non-Spherical Particles[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(5): 1330-1338.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 序号 | 装填轴向位置 l0/mm | 水平轴向堆积长 度L/mm | 坡状堆积坡度角 α/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 293.3 | 22.01 |
| 2 | 40 | 264.6 | 21.22 |
| 3 | 70 | 229.7 | 20.73 |
| 4 | 100 | 203.8 | 19.82 |
Table 1 Characteristic parameters of propellant pellet stacking
| 序号 | 装填轴向位置 l0/mm | 水平轴向堆积长 度L/mm | 坡状堆积坡度角 α/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 293.3 | 22.01 |
| 2 | 40 | 264.6 | 21.22 |
| 3 | 70 | 229.7 | 20.73 |
| 4 | 100 | 203.8 | 19.82 |
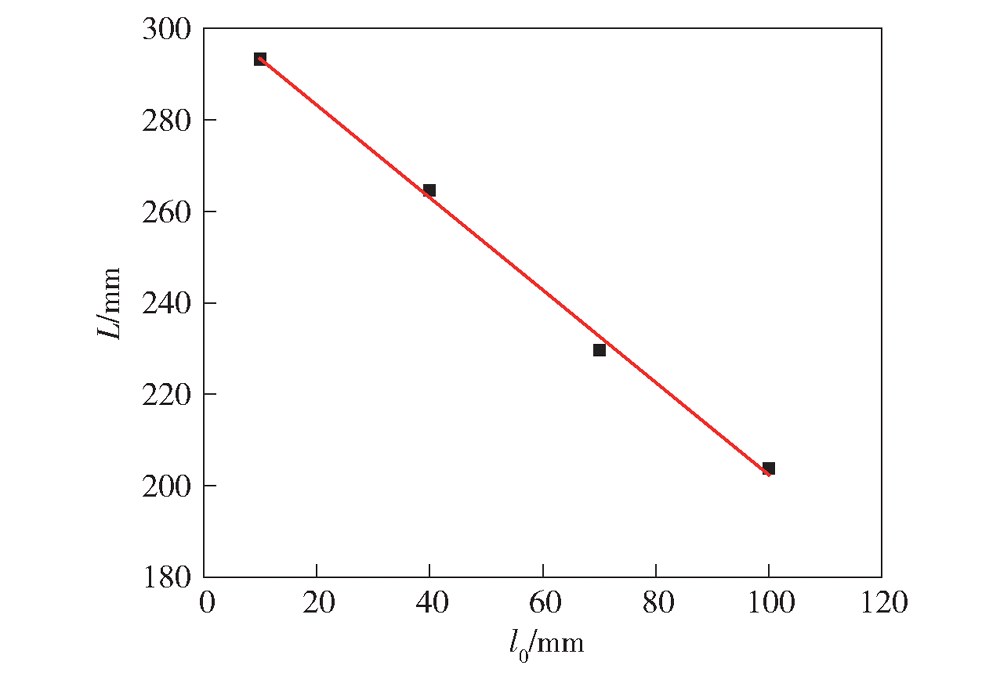
Fig.13 Relationship between the axial length of the horizontal stacking of propellant pellets and the horizontal loading position of the modular cartridge
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
陆中兵, 周彦煌, 丁珏, 等. 模块装药膛内火焰扩散过程的理论研究[J]. 弹道学报, 1998, 10(3): 6-10.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陆中兵, 周彦煌. 模块装药火炮膛内两相燃烧模型及压力波模拟[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1999, 19(3): 269-273.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
王育维, 魏建国, 郭映华, 等. 模块装药压力波数值模拟[J]. 火炮发射与控制学报, 2000(4): 1-5.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
王育维, 郭映华, 董彦诚, 等. 可燃容器对小号模块装药压力波影响的研究[J]. 火炮发射与控制学报, 2016, 37(2): 31-35.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
马华庆, 赵永志. 喷动流化床中杆状颗粒混合特性的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2020, 54(7): 1347-1354.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.032 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1002/aic.14636 URL |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.10.046 URL |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.07.099 URL |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.220 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/ceat.v32:3 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.03.046 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2016.08.015 URL |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2015.11.045 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2018.08.041 URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.12.066 URL |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2022.117431 URL |
| [19] |
陈安, 余永刚. 两模块装药点传火过程及药粒散布特性[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(7): 39-49.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
陈安, 余永刚. 单模块装药点传火过程中药粒散布模拟试验与仿真[J]. 含能材料, 2020, 28(8): 731-739.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
任冰. 稠密气固系统非球形颗粒运动机制的试验和CFD-DEM耦合模拟研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2013.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
王国强, 郝万军, 王继新. 离散单元法及其在EDEM上的实践[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2010.
|
|
|
| [1] | XIAO Wangang, ZHOU Yunbo, FU Yaoyu, ZHANG Ming, ZHOU Jun, GE Jitao. Analysis of the Influence of Soil on the Maneuverability of Military Off-road Vehicles [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(1): 288-298. |
| [2] | HUANG Wenkuan, QIAN Linfang, YIN Qiang, LIU Taisu. Fault Diagnosis Method of Modular Charge Feeding Mechanism Based on Transfer Learning [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(10): 2964-2974. |
| [3] | WANG Mingming, QIAN Linfang, CHEN Guangsong, LIU Taisu. Uncertainty Analysis of Ammunition Ramming Process Based on Probability Density Evolution Method [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(6): 1215-1224. |
| [4] | LI Wei, HAN Chongwei, LIU Aifeng, REN Haibo, HU Xin, JIANG Junfeng. Modeling and Simulation of Self-stable Gun Line Control Using Interference Rate Compesation [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(6): 1233-1245. |
| [5] | SHAN Chunlai, LIU Pengke, GU Bin, HE Qi, XU Hongying. Application of Multilevel Optimization Algorithm in Artillery Integrated Design [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(1): 11-19. |
| [6] | CHENG Shenshen, TAO Ruyi, WANG Hao, XUE Shao, LIN Qingyu. Dampling Characteristics of Projectile in Engraving Process of Nylon Sealing Band [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(9): 1847-1857. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jin, WANG Xuebin, SHI Wenze, DONG Zihua, DENG Haifei. Detection Method for Chamber of Large-caliber Artillery Barrel Based on Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Surface SH-wave [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(8): 1763-1770. |
| [8] | MIAO Wei, YIN Qiang, QIAN Linfang. An Approximate Calculation Method for Ejection of Propellant Gas during After-effect Period of Artillery [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(7): 1381-1391. |
| [9] | DING Shukui, WANG Liangming, YANG Zhiwei, DING Xuran. Dynamic Property of the Initial Disturbance of Projectile for the Long-range Artillery Howitzer [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(4): 673-683. |
| [10] | ZHANG Cheng, LIU Zhaoyang, GU Keqiu. Buffering Mechanism and Characteristic Optimization of Ultra-light Artillery Backtrail [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(9): 1752-1761. |
| [11] | LIU Taisu, QIAN Linfang, CHEN Guangsong. Robust Optimal Design of a Propellant Transport Mechanism for In-place Consistency with Small-angle Propellant Transport [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(8): 1473-1482. |
| [12] | QIAN Linfang, CHEN Guangsong, WANG Mingming. The Effects of Initial State Parameters of Projectiles at Muzzle on Their Ground Dispersion [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(5): 833-841. |
| [13] | XIE Jietao, WU Juan, WANG Shu'en, FAN Zhaojun, HAN Baigang. Test Method for Judging Kill Probability of Anti-aircraft Artillery by Quantity of Killed Targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(4): 634-640. |
| [14] | JIN Wenqi, NING Jingui, WANG Jian, DENG Bo. Simulation Research of Interior Ballistics Based on Erosion Wear Characteristic of Full-bore [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(5): 968-977. |
| [15] | ZHANG Peizhong, NING Jingui, WANG Jianguo, WANG Xin. Research on the Stealth Performance of Half-stealth Projectile against Radar [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(12): 2587-2592. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
