


主管单位:中国科学技术协会
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



兵工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (10): 250424-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2025.0424
葛朴昕1, 宋子豪1, 李志洋1, 王海任2, 雷建银1,3,*( ), 刘志芳1
), 刘志芳1
收稿日期:2025-05-29
上线日期:2025-11-05
通讯作者:
基金资助:
GE Puxin1, SONG Zihao1, LI Zhiyang1, WANG Hairen2, LEI Jianyin1,3,*( ), LIU Zhifang1
), LIU Zhifang1
Received:2025-05-29
Online:2025-11-05
摘要:
在爆炸载荷作用下,预测结构响应的关键在于准确建立输入载荷、材料性能与力学响应之间的关系。提出了一种结合数据驱动和量纲不变性分析的方法,用于识别在脉冲载荷作用下圆板动态塑性响应中的关键无量纲参数,并构建挠度预测模型。通过在ABAQUS中建立固支圆板的显式动力学模型,设置圆板半径L、厚度H、密度ρ、屈服强度σ0及脉冲冲量I为变量生成数据;以人工神经网络拟合响应面并求梯度,结合指数矩阵法与主动子空间分析完成特征构造与降维,识别主导无量纲量。结果表明,通过指数矩阵耦合和主动子空间分析,最终将五个原始变量表示为Johnson损伤数I2/(ρσ0H2)与几何参数H/L的组合,将问题从多维输入降维至一个核心变量。识别的无量纲量能有效表征冲击损伤和动力响应,并展现出良好的适用性。研究成果为冲击动力学问题提供了一种高效的数据驱动分析工具,体现了机器学习在工程物理问题中可能的应用前景。
葛朴昕, 宋子豪, 李志洋, 王海任, 雷建银, 刘志芳. 基于数据驱动的均匀脉冲载荷作用下低碳钢圆板动力学响应的量纲分析[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(10): 250424-.
GE Puxin, SONG Zihao, LI Zhiyang, WANG Hairen, LEI Jianyin, LIU Zhifang. Data-Driven Dimensional Analysis of the Dynamic Response of Low-Carbon Steel Circular Plates under Uniform Impulsive Loading[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(10): 250424-.
| ρ/(g·mm-3) | E/MPa | ν | σo/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.007861 | 207×103 | 0.3 | 233 |
表1 低碳钢材料参数
Table 1 Low-carbon steel parameters
| ρ/(g·mm-3) | E/MPa | ν | σo/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.007861 | 207×103 | 0.3 | 233 |
| 参数 | 符号 | 下限 | 上限 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 半径 | L/mm | 27.03 | 36.57 |
| 厚度 | H/mm | 1.64 | 2.22 |
| 密度 | ρ/(g·mm-3) | 0.00663 | 0.00897 |
| 脉冲载荷 | I/(N·ms) | 3150 | 7150 |
| 屈服强度 | σ0/MPa | 189.55 | 256.45 |
表2 数据集参数变动范围
Table 2 Parameter variation range for the dataset
| 参数 | 符号 | 下限 | 上限 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 半径 | L/mm | 27.03 | 36.57 |
| 厚度 | H/mm | 1.64 | 2.22 |
| 密度 | ρ/(g·mm-3) | 0.00663 | 0.00897 |
| 脉冲载荷 | I/(N·ms) | 3150 | 7150 |
| 屈服强度 | σ0/MPa | 189.55 | 256.45 |

图4 均匀脉冲载荷作用下低碳钢圆板动力学响应的数据驱动量纲分析示意图
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of the data-driven dimensional analysis of the dynamic response of a low-carbon steel circular plate under uniform pulse load
| 物理量 | 符号 | 量纲向量[M,L,T] |
|---|---|---|
| 密度/(g·mm-3) | ρ | [1,-3,0] |
| 初始屈服强度/(N·mm-2) | σ0 | [1,-1,-2] |
| 半径/mm | L | [0,1,0] |
| 厚度/mm | H | [0,1,0] |
| 单位面积所受脉冲/(N·ms·mm-2) | I | [1,-1,-1] |
表3 脉冲载荷下圆板中的量纲向量
Table 3 Dimensional vector in a circular plate under pulse loading
| 物理量 | 符号 | 量纲向量[M,L,T] |
|---|---|---|
| 密度/(g·mm-3) | ρ | [1,-3,0] |
| 初始屈服强度/(N·mm-2) | σ0 | [1,-1,-2] |
| 半径/mm | L | [0,1,0] |
| 厚度/mm | H | [0,1,0] |
| 单位面积所受脉冲/(N·ms·mm-2) | I | [1,-1,-1] |
| 隐藏层 | 神经元数 | 激活函数 | 损失函数 | 优化器 | 批量大小 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | ReLU/Tanh | MAE | Adam | 32 |
表4 神经网络参数
Table 4 Neural network parameter
| 隐藏层 | 神经元数 | 激活函数 | 损失函数 | 优化器 | 批量大小 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | ReLU/Tanh | MAE | Adam | 32 |
| 数据集 | 样本数 | MSE | R2 | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 700 | 0.021382 | 0.9981 | 0.073878 |
| 验证集 | 150 | 0.056340 | 0.9952 | 0.092583 |
| 测试集 | 150 | 0.037933 | 0.9974 | 0.089986 |
表5 训练集、验证集与测试集性能对比
Table 5 Comparison of training, validation, and test set performance
| 数据集 | 样本数 | MSE | R2 | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 700 | 0.021382 | 0.9981 | 0.073878 |
| 验证集 | 150 | 0.056340 | 0.9952 | 0.092583 |
| 测试集 | 150 | 0.037933 | 0.9974 | 0.089986 |
| 模型 | 输入特征 | R2 | MAE/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| FE-1 | ($\frac{{I}^{2}}{\rho {\sigma }_{0}{H}^{2}}$,$\frac{H}{L}$) | 0.97 | 19.7 |
| FE-2 | ($\frac{{I}^{2}}{\rho {\sigma }_{0}{L}^{2}}$,$\frac{H}{L}$) | 0.88 | 33.3 |
表6 基于不同特征组合的特征模型质量评估
Table 6 Quality assessment of feature models based on different feature combinations
| 模型 | 输入特征 | R2 | MAE/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| FE-1 | ($\frac{{I}^{2}}{\rho {\sigma }_{0}{H}^{2}}$,$\frac{H}{L}$) | 0.97 | 19.7 |
| FE-2 | ($\frac{{I}^{2}}{\rho {\sigma }_{0}{L}^{2}}$,$\frac{H}{L}$) | 0.88 | 33.3 |
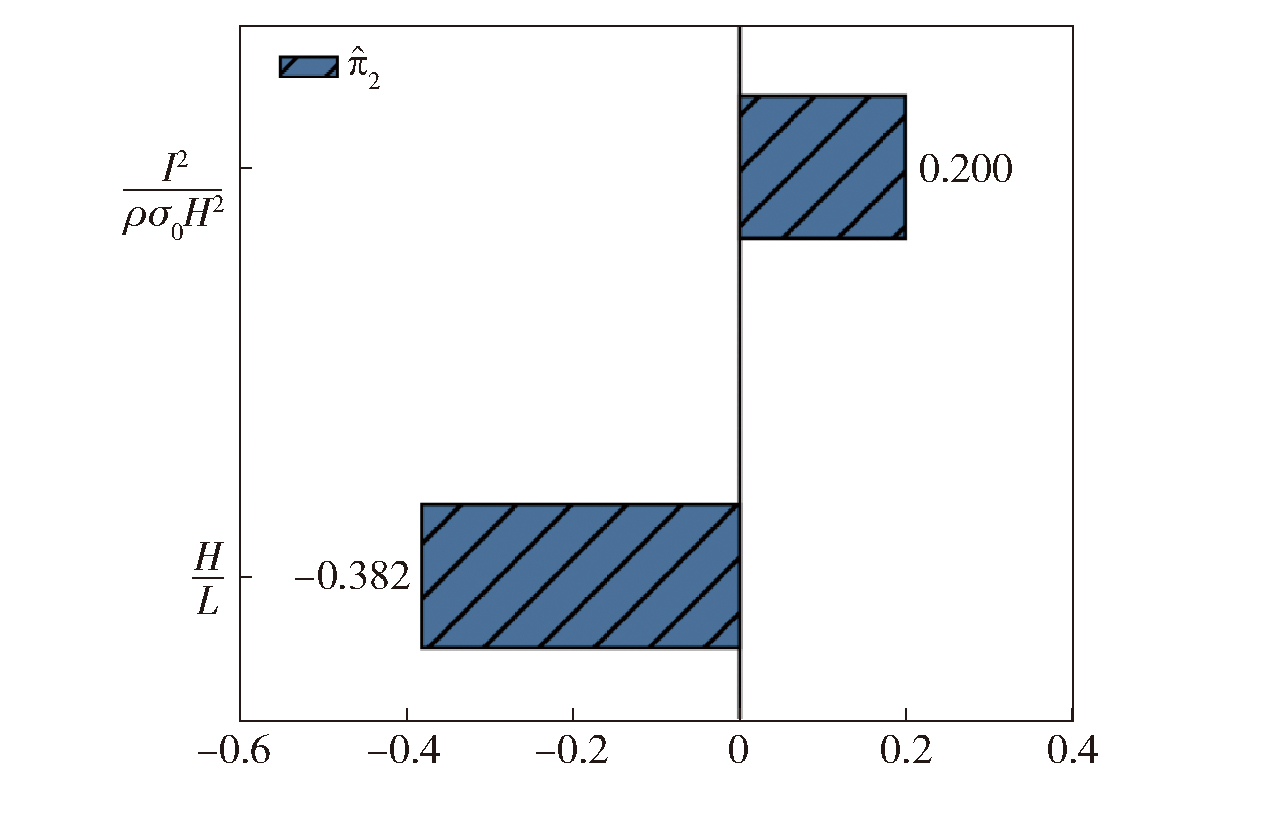
图10 低碳钢圆板在均匀脉冲载荷下的两项无量纲参数表征
Fig.10 Two dimensionless parameters characterizing a low-carbon steel circular plate subjected to a uniform impulsive load
| 方程 | $\frac{W}{H}$=a(($\frac{{I}^{2}}{\rho {\sigma }_{0}{H}^{2}}$)0.200($\frac{H}{L}$)-0.382)b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数 | a | b | R2 | MSE |
| 数值 | 0.558 | 2.361 | 0.9703 | 0.249 |
表7 板中心挠厚比对应预测公式
Table 7 Prediction formula for the deflection-to-thickness ratio at the center of the plate
| 方程 | $\frac{W}{H}$=a(($\frac{{I}^{2}}{\rho {\sigma }_{0}{H}^{2}}$)0.200($\frac{H}{L}$)-0.382)b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数 | a | b | R2 | MSE |
| 数值 | 0.558 | 2.361 | 0.9703 | 0.249 |

图12 均匀脉冲载荷下低碳钢圆盘中载荷强度I与 挠厚比关系图
Fig.12 Graph of the relationship between load intensity I and the deflection-to-thickness ratio in a low-carbon steel disc under uniform impulse loading
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
剡小军, 孙浩, 马林, 等. 水下爆炸作用下典型舰船目标毁伤特性[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(S2): 215-221.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
蒋欣利, 张国凯, 何勇, 等. 密闭建筑温压炸药内爆炸后燃效应[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(8): 2520-2530.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
潘美霖, 彭卫文, 冷春江, 等. 基于贝叶斯深度学习的复杂结构爆炸载荷的快速估计[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2025, 45(8): 084201.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
王娟, 慈林林, 姚康泽. 特征选择方法综述[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2005, 27(12): 68-71.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [1] | 施琦, 茅云生, 水金朋, 陈柳屹, 梁棋钰, 宋利飞. 爬壁机器人矩形闭环磁阵列吸附模块改进与优化[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(9): 241013-. |
| [2] | 甄泓, 肖李军, 杜成鑫, 宋卫东. 在弹道冲击条件下超高分子量聚乙烯纤维复合材料板破坏模式[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(7): 240725-. |
| [3] | 陈军, 佟龑, 牛轶峰, 于宏渤, 李霓, 张馨予. 模糊认知图研究进展及其在无人系统中的应用[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(7): 240804-. |
| [4] | 王艺臻, 尹建平, 张雪朋, 伊建亚, 李旭东. 聚能射流动态侵彻威力预测模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(6): 240932-. |
| [5] | 宁建国, 汪齐, 栗建桥. 基于人工神经网络的三棱柱定向装药结构破片初速预测模型[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(3): 240346-. |
| [6] | 张骢, 陆俊桦, 岳明凯. 成像引信仿生复合减振结构设计与仿真[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(2): 240021-. |
| [7] | 李洋军, 黄琦龙, 杨力, 陈旭. 数据和知识双驱动的空中集群目标作战意图识别[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(2): 240113-. |
| [8] | 李祥辉, 张兴渝, 胡家豪, 刘洋, 马伯翰, 王永刚, 蒋招绣. AISI 4340钢靶大塑性模型及断裂起始模型参数研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(1): 231210-. |
| [9] | 高茂国, 刘睿, 郭岩松, 耿恒恒, 陈鹏万. HfZrTiTaAl系高熵合金动态变形、损伤及破坏行为[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(1): 231183-. |
| [10] | 吴春尧, 宋春明, 李干, 徐观淦, 韩彤. 高压膜片破膜压力阈值及影响因素[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(9): 3307-3316. |
| [11] | 左铭朔, 徐豫新, 李永鹏, 李旭东, 郭德龙, 杨祥. 内爆载荷下民机用定向泄爆容器结构的动态响应[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(7): 2383-2392. |
| [12] | 贾晶晶, 张治民, 于建民, 薛勇, 吴昂. 基于响应面法的轻质尾翼均匀挤压成形数值模拟及模具结构优化[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(6): 1824-1839. |
| [13] | 王伽豪, 那文波, 刘志威, 昝琪, 王铮. 双闭环比值控制系统传感器故障诊断方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(4): 1252-1263. |
| [14] | 高健, 邹利波, 于存贵. 基于相场耦合内聚力模型的身管镀层剥落数值模拟[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(11): 4081-4093. |
| [15] | 周宏根, 任小蝶, 孙丽, 李国超, 文思钊, 彭展, 刘寅飞. JUST回转支承故障试验数据分析[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(10): 3744-3753. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4
京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4