


主管单位:中国科学技术协会
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



兵工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (7): 240611-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2024.0611
胡木林1, 武毅1,2,*( ), 王行远1, 郭松林1, 于俊艺1
), 王行远1, 郭松林1, 于俊艺1
收稿日期:2024-07-22
上线日期:2025-08-12
通讯作者:
基金资助:
HU Mulin1, WUYi1,2,*( ), WANG Xingyuan1, GUO Songlin1, YU Junyi1
), WANG Xingyuan1, GUO Songlin1, YU Junyi1
Received:2024-07-22
Online:2025-08-12
摘要:
混合工艺作为固体推进剂制备的重要工序,一般是指将Al、AP、RDX等颗粒相加入到高分子黏合剂基体中,经机械捏合、搅拌使黏合剂浆料涂敷在固体粒子表面的过程。基于Mixture固-气-液多相流模型,进行固体颗粒相加注混合釜中的扩散伴随桨叶动态捏合过程的数值仿真研究。开展不同固含量(0%~95%)药浆的动态流变测量实验,构建了药浆流变模型;考虑颗粒浓度动态变化对局部流变特性影响,开展了不同颗粒加注流量的混合动态过程仿真。分析不同工况条件下颗粒浓度、压力场和扭矩随时间的变化规律。实验结果表明:建立的数值仿真方法与文献实验结果对比,平均误差在15%内,具有良好的一致性;混合过程中近、远桨叶叶尖处的挤压力最大,而叶中部存在低压区;混合过程中,桨叶扭矩呈锯齿状波动变化,随着颗粒相的加注,扭矩逐渐增大;固体颗粒相加注流量小幅增大时,扭矩变化较小;加注流量大幅增大时,扭矩增幅可达90%。连续加料混合过程中远心桨的扭矩值持续上升,最终平均值可达初始阶段的19倍。所得成果可为固体推进剂的混合工艺效率提升和安全性研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
胡木林, 武毅, 王行远, 郭松林, 于俊艺. HTPB/Al/AP/RDX固体推进剂动态混合过程数值仿真[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(7): 240611-.
HU Mulin, WUYi, WANG Xingyuan, GUO Songlin, YU Junyi. Numerical Simulation of the Dynamic Mixing Process of HTPB/Al/AP/RDX Solid Propellant[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(7): 240611-.
| 组别 | Al粉/% | AP/% | RDX/% | HTPB/% | 固含量 /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| b | 18 | 7 | 0 | 75 | 25 |
| c | 18 | 42 | 0 | 40 | 60 |
| d | 18 | 46 | 31 | 5 | 95 |
表1 流变实验药浆组成与含量
Table 1 Composition and content of rheological experimental propellant slurry
| 组别 | Al粉/% | AP/% | RDX/% | HTPB/% | 固含量 /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| b | 18 | 7 | 0 | 75 | 25 |
| c | 18 | 42 | 0 | 40 | 60 |
| d | 18 | 46 | 31 | 5 | 95 |
| 序号 | 入口数 | 粉末加注 速度mm/s | 工序 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 12.5 | 加注+混合46.8s |
| 2 | 15 | 15 | 加注+混合39s |
| 3 | 15 | 17.5 | 加注+混合33.43s |
| 4 | 15 | 20 | 加注+混合29.25s |
| 5 | 7 | 32.5 | 加注+混合39s |
| 6 | 15 | 15 | 加注+混合Al粉7.45s |
| 混合直至均匀 | |||
| 加注+混合AP 24.89s | |||
| 混合直至均匀 | |||
| 加注+混合RDX 6.66s | |||
| 混合直至均匀 |
表2 工况设置
Table 2 Working condition settings
| 序号 | 入口数 | 粉末加注 速度mm/s | 工序 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 12.5 | 加注+混合46.8s |
| 2 | 15 | 15 | 加注+混合39s |
| 3 | 15 | 17.5 | 加注+混合33.43s |
| 4 | 15 | 20 | 加注+混合29.25s |
| 5 | 7 | 32.5 | 加注+混合39s |
| 6 | 15 | 15 | 加注+混合Al粉7.45s |
| 混合直至均匀 | |||
| 加注+混合AP 24.89s | |||
| 混合直至均匀 | |||
| 加注+混合RDX 6.66s | |||
| 混合直至均匀 |
| 组成 | 黏合剂 (液相) | AL颗粒相 (d=10μm) | AP颗粒相 (d=100μm) | RDX颗粒相 (d=100μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量% | 24 | 18 | 46 | 12 |
表3 固体推进剂药浆组成与含量
Table 3 Composition and content of solid propellant slurry
| 组成 | 黏合剂 (液相) | AL颗粒相 (d=10μm) | AP颗粒相 (d=100μm) | RDX颗粒相 (d=100μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量% | 24 | 18 | 46 | 12 |
| 组别 | 网格数 | 远心桨扭矩/(N·m) | 偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 网格1 | 2×105 | 0.000295 | -8.3 |
| 网格2 | 3×105 | 0.000321 | -0.3 |
| 网格3 | 4×105 | 0.000324 | 0.6 |
| 网格4 | 7×105 | 0.000322 | 0 |
表4 不同网格数远心桨扭矩对时间平均值
Table 4 Time averaged values of centrifugal propeller torque with different grid numbers
| 组别 | 网格数 | 远心桨扭矩/(N·m) | 偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 网格1 | 2×105 | 0.000295 | -8.3 |
| 网格2 | 3×105 | 0.000321 | -0.3 |
| 网格3 | 4×105 | 0.000324 | 0.6 |
| 网格4 | 7×105 | 0.000322 | 0 |

图11 不同加注流量20s时刻混合釜内与20mm高度横截面压强、颗粒浓度分布
Fig.11 Distribution of pressure and particle concentration in the mixing pot at 20s at different injection speeds:in the mixing pot,at the cross section with a height of 20mm
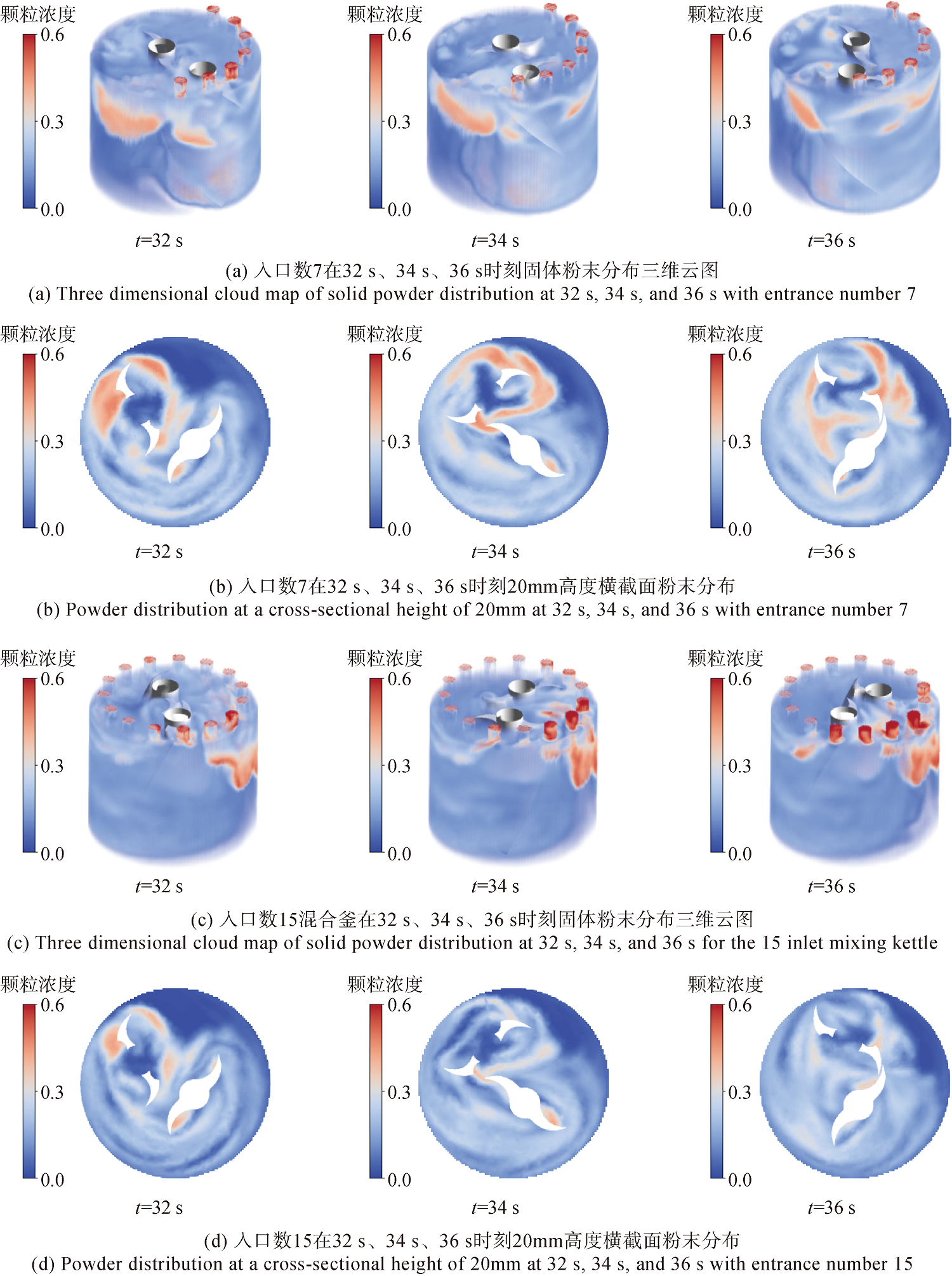
图13 入口数7和入口数15混合釜在32s、34s、36s时刻固体粉末分布三维云图与20mm高度横截面粉末分布
Fig.13 Particle distributions in the mixing pot and at the cross section with a height of 20mm with 7 inlets and 15 inlets at 32s,34s,and 36s
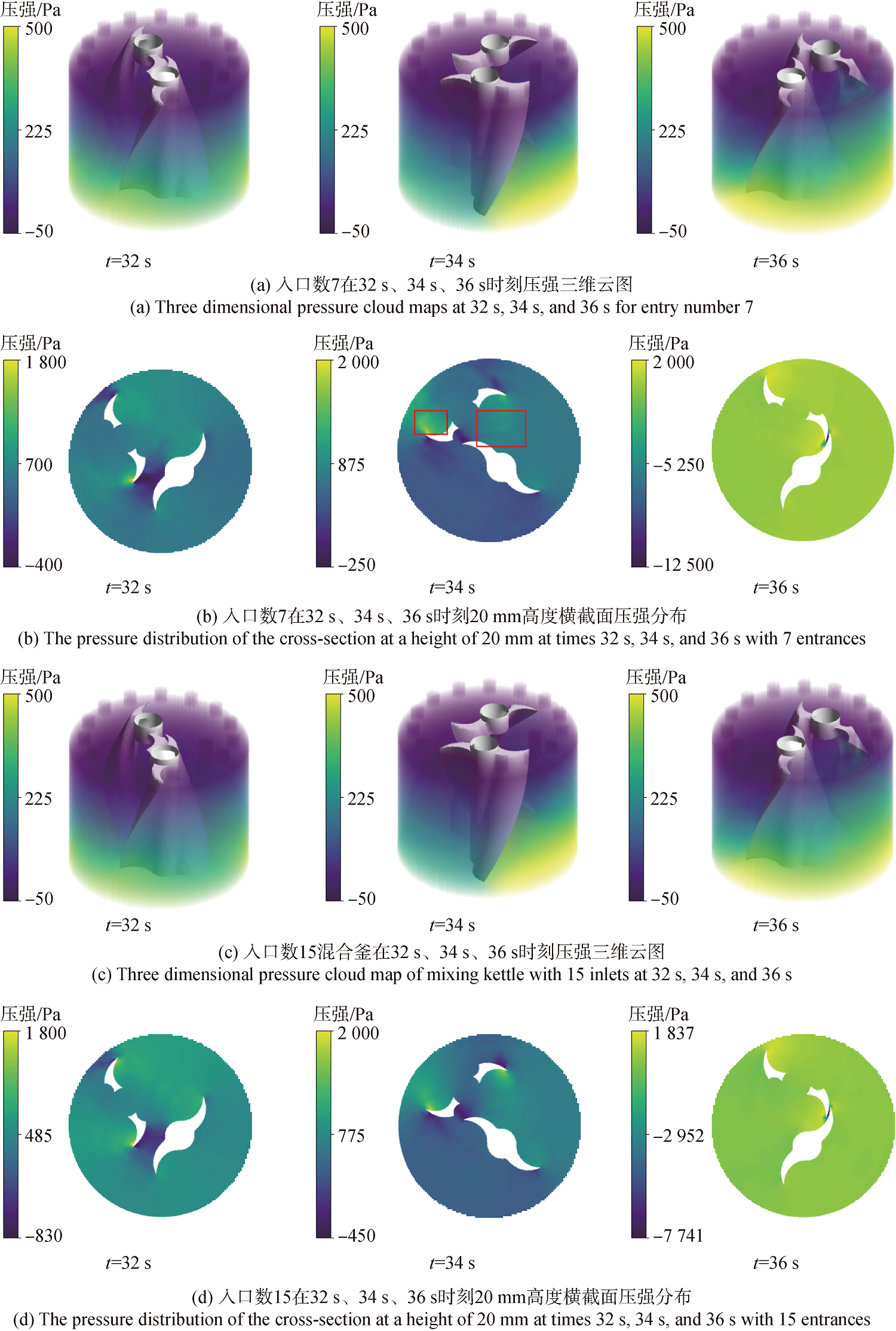
图14 入口数7和入口数15混合釜在32s、34s、36s时刻压强三维云图与20mm高度横截面压强分布
Fig.14 Pressure distributions in the mixing pot and at the cross section with a height of 20mm with 7 inlets and 15 inlets at 32s,34s,and 36s
| 曲线编号 | 扭矩平均值/(N·m) | 与曲线I相比增幅/% |
|---|---|---|
| I | 0.033299 | |
| II | 0.091416 | 174.5 |
| III | 0.175965 | 428.4 |
| IV V VI | 0.506172 0.489363 0.639475 | 1420.1 1369.6 1820.4 |
表5 I~VI曲线远心桨扭矩平均值
Table 5 I-VI curve average value of centrifugal propeller torque
| 曲线编号 | 扭矩平均值/(N·m) | 与曲线I相比增幅/% |
|---|---|---|
| I | 0.033299 | |
| II | 0.091416 | 174.5 |
| III | 0.175965 | 428.4 |
| IV V VI | 0.506172 0.489363 0.639475 | 1420.1 1369.6 1820.4 |
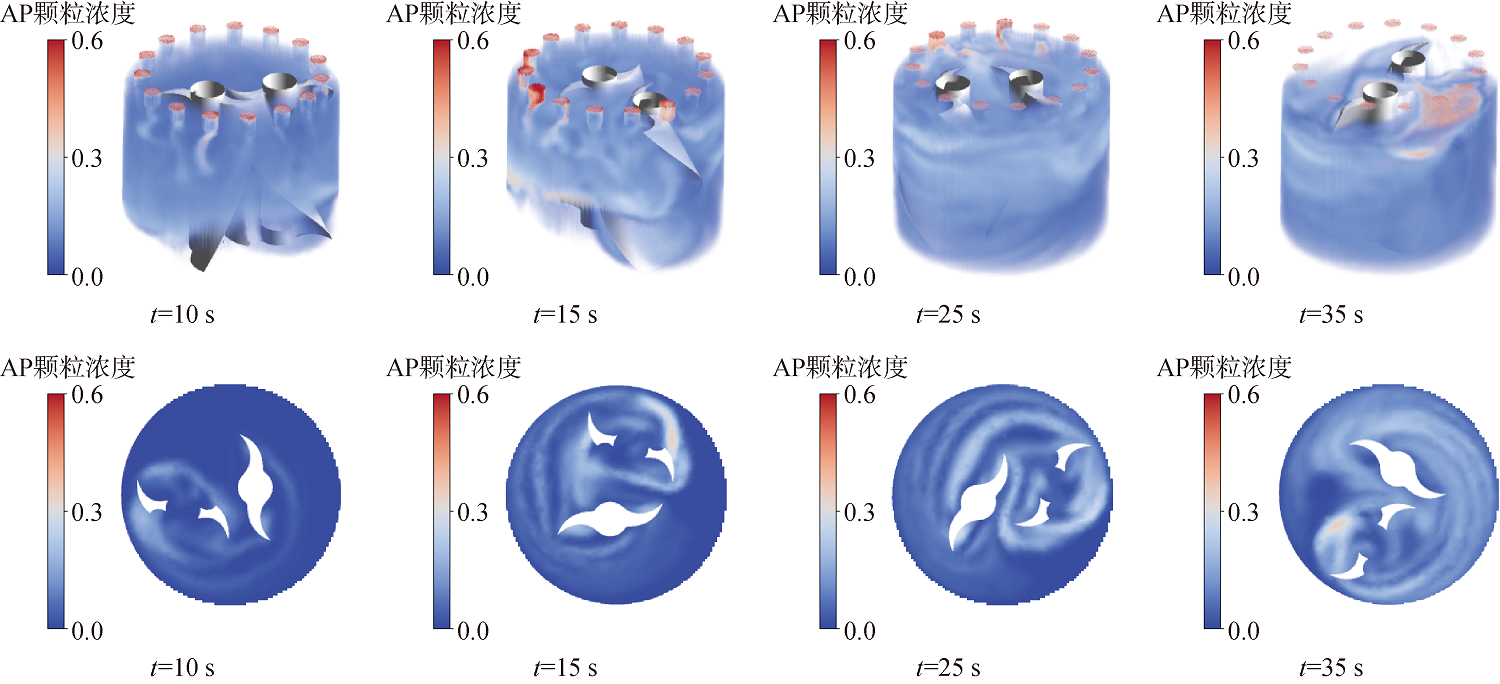
图17 III阶段AP颗粒分布三维云图(上)与20mm高度处平面分布云图(下)
Fig.17 Three-dimensional cloud map of AP particle distribution in Stage III (upper) and plane distribution cloud map at a height of 20mm(below)
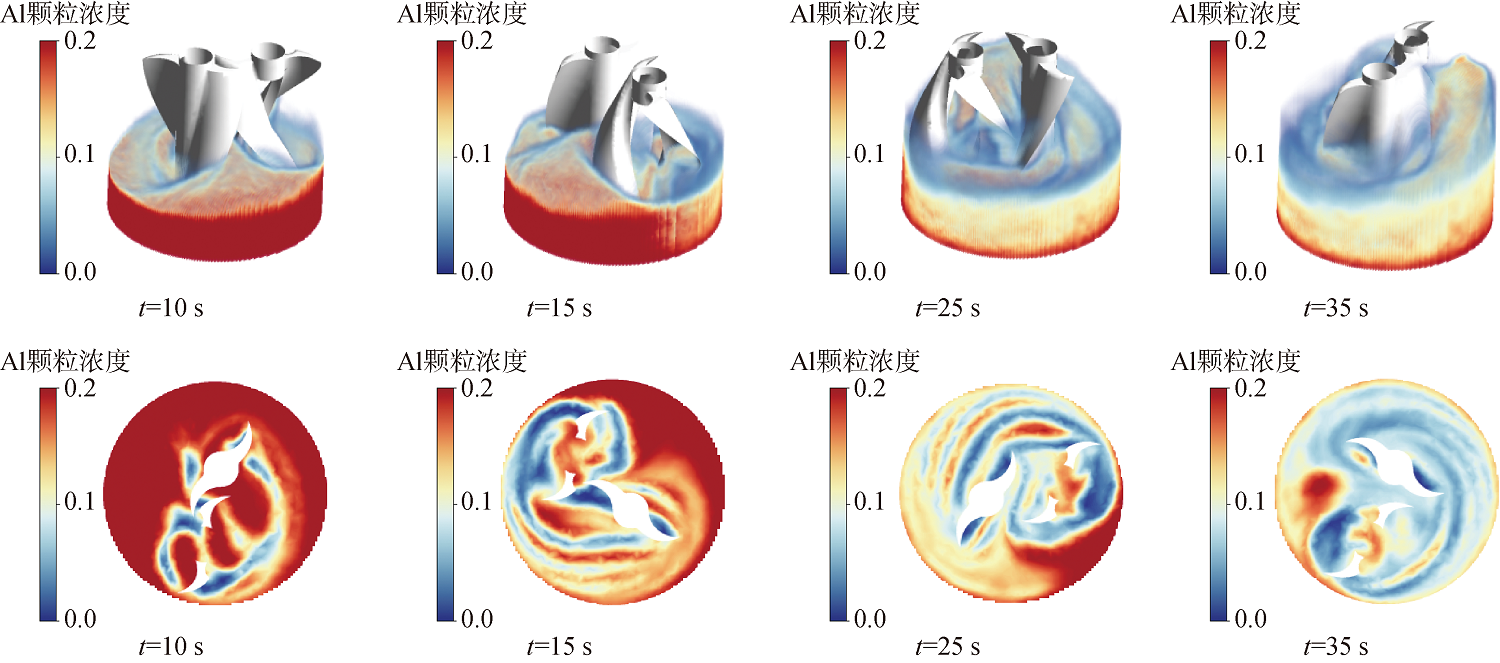
图18 III阶段Al颗粒分布三维云图(上)与20mm高度处平面分布云图(下)
Fig.18 Three-dimensional cloud map of Al particle distribution in Stage III (upper) and plane distribution cloud map at a height of 20mm(below)

图19 V阶段AP颗粒分布三维云图(上)与40mm高度处平面分布云图(下)
Fig.19 Three dimensional cloud map of AP particle distribution in Stage V (upper) and plane distribution cloud map at a height of 40mm(below)
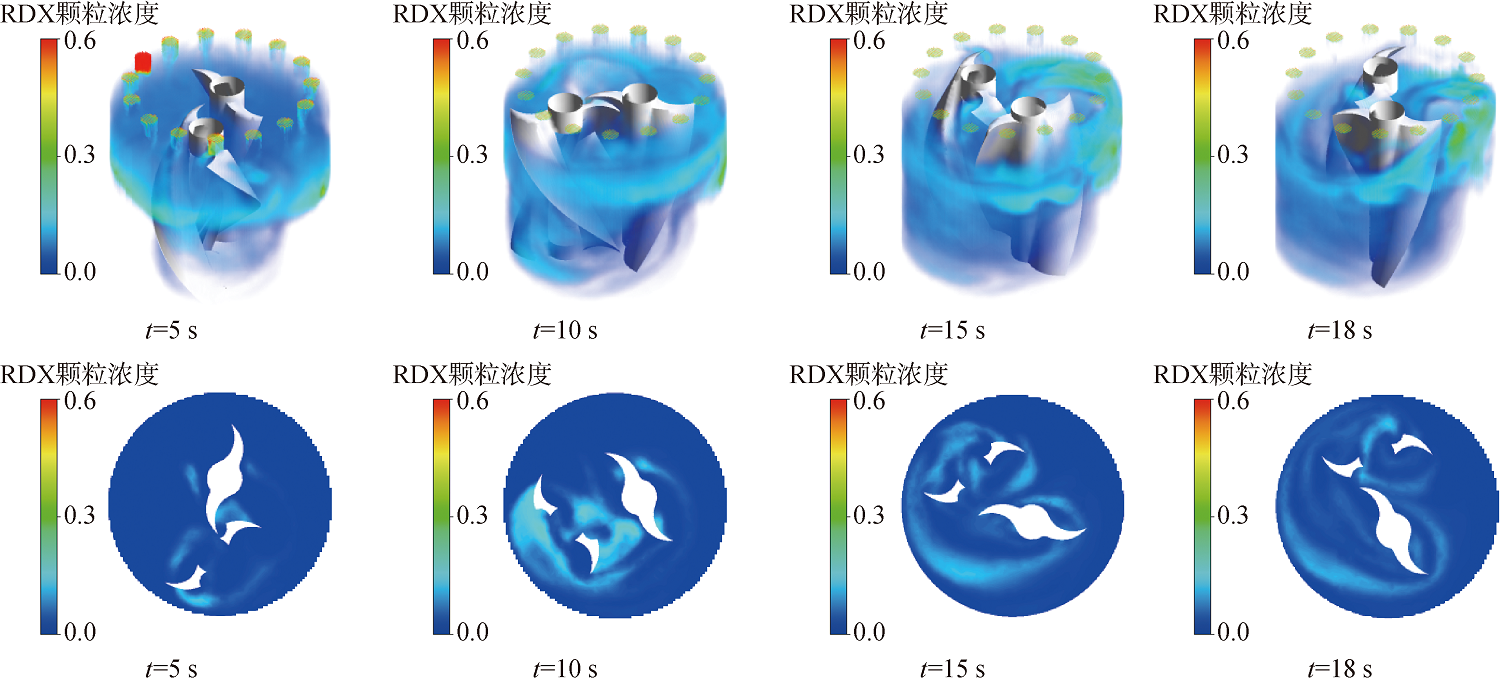
图20 V阶段RDX颗粒分布三维云图(上)与40mm高度处平面分布云图(下)
Fig.20 Three-dimensional cloud map of RDX particle distribution in Stage V (upper) and plane distribution cloud map at a height of 40mm(below)
| [1] |
李莹新, 莫纪安, 王秀云, 等. 固体火箭发动机壳体复合材料研究进展[J]. 航天制造技术, 2020(4):65-69.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
时茗扬, 李春娜, 刘洋, 等. 不确定性下的固体火箭发动机性能精确代理建模方法[J]. 推进技术, 2025, 46(1):32-41.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
朱艳明, 吕端, 胡润芝, 等. 固体推进剂连续混合工艺参数控制与工程优化[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2020, 43(6):776-781.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
武宇恒, 蔚红建, 付小龙. 固体推进剂的流变性能及工艺仿真研究进展[J]. 火工品, 2024 (2):58-64.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
关英波. 立式捏合机搅拌桨叶的力学数值分析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2007.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
景玲. 立式捏合机搅拌桨叶应力与温度数值分析研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2013.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
徐江华. 立式捏合机搅拌桨叶的转矩数值分析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
易朋兴, 胡友民, 崔峰, 等. 立式捏合机捏合间隙影响CFD分析[J]. 化工学报, 2007, 58(10):2680-2684.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
吴玉金, 野延年. 混合生产中固体推进剂的安全问题[J]. 固体火箭技术, 1998 (4):53-55.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
李胜婷, 庞维强, 南风强, 等. 不同因素对固体推进剂流变性能影响研究进展[J]. 火炸药学报, 2024, 47(2):114-130.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
李胜婷, 庞维强, 南风强, 等. 复合固体推进剂药浆浇铸工艺仿真及优化[J]. 火炸药学报, 2024, 47(10):937-944.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
朱宏春, 王吉强, 苗建波. NEPE推进剂药浆固化初期特殊流变性能研究[J]. 推进技术, 2013, 34(10):1420-1425.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
杜幸, 刘晋湘, 陈江波, 等. 丁羟推进剂流变性研究[J/OL]. 火炸药学报, 2025[2025-07-10].https://doi.org/10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202303035.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
江晓瑞, 李卓, 鲁荣, 等. 丁羟推进剂药浆固化过程中触变性转变规律研究[J]. 推进技术, 2020, 41(5):1178-1184.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
潘新洲, 李尚文, 姜磊, 等. 少铝HTPE推进剂药浆流变特性研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2021, 44(5):656-661.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
江晓瑞, 李卓, 韩秀洁, 等. 固体推进剂药浆改进Herschel-Bukely模型及其在仿真分析中的应用[J]. 推进技术, 2019, 40(9):2137-2143.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00532 pmid: 35647447 |
| [25] |
梁建, 朱剑波, 段丽华, 等. 立式捏合机桨叶结构与桨叶变形量的CFD仿真[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2018, 41(6):745-749,753.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
杨明金. 立式捏合机混合釜内固体推进剂药浆混合的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2008.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
洪寅, 刘看, 武毅, 等. 固体推进剂药浆立式混合过程SPH方法研究[J]. 含能材料, 2024, 32(11):1162-1173.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
王建, 刘皓, 赵亚风, 等. 复合固体推进剂双螺杆挤出成型过程DEM-CFD耦合仿真[J]. 含能材料, 2022, 30(2):138-145.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
敖维坚, 张立新, 苏昌银, 等. 复合推进剂装药混合中的扭矩安全值[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2020, 43(1):53-58.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
张力恒, 苏昌银, 何煜, 等. 推进剂装药混合过程安全性研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2012, 35(4):508-512.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
王正方, 翟瑞清. 立式捏合机搅拌桨的设计[J]. 固体火箭技术, 1993(1):65-69.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [1] | 王鑫, 吴艳青, 杨昆, 武毅, 侯晓. 破片撞击高能推进剂装药爆燃机理实验研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(3): 240293-. |
| [2] | 李玉雪, 田小涛, 马伊凡, 刘佩进, 严启龙. 不同粒径黑火药点火过程中与纤维素壳体材料的热相互作用[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(5): 1582-1592. |
| [3] | 席运志, 李军伟, 陈雪莉, 韩磊, 王宁飞. 基于旋转阀的固体推进剂压强耦合响应测试方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(3): 511-520. |
| [4] | 侯宇菲, 许进升, 周长省, 陈雄, 李宏文. 复合固体推进剂颗粒与基体初始界面有无缺陷的细观模型对比[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(9): 1800-1808. |
| [5] | 张正金, 郭效德, 刘杰, 梁力, 李宽宽, 夏亮, 常志鹏, 田淑宝, 黄东彦, 杨雪芹. 超细亚铁氰化铅/高氯酸铵复合粒子的制备及热分解、防团聚性能研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(11): 2220-2228. |
| [6] | 叶振威, 余永刚. 脉冲点火射流与高氯酸铵/端羟基聚丁二烯固体推进剂耦合燃烧的试验研究及数值模拟[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(8): 1507-1514. |
| [7] | 王鸿丽, 许进升, 刘宗魁, 童心, 周长省. 复合改性双基推进剂黏弹性-黏塑性-黏损伤本构模型研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(7): 1308-1315. |
| [8] | 张怀龙, 菅晓霞, 周伟良, 肖乐勤. 固体火箭推进剂的模拟低温点火冲击试验加载方法研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(4): 717-723. |
| [9] | 齐晓飞, 谢五喜, 严启龙, 刘庆, 刘春. 中性聚合物键合剂与奥克托今的界面作用[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(10): 1942-1949. |
| [10] | 李文凤, 余永刚, 叶锐. 装药尺寸对高氯酸铵/端羟基聚丁二烯底排药烤燃特性的影响[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(8): 1532-1540. |
| [11] | 徐义华, 胡旭, 邹昊, 李雨林, 曾卓雄. 基于多层氧化层结构的硼颗粒点火模型研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(12): 2242-2250. |
| [12] | 李吉祯, 樊学忠, 张国防, 蔚红建, 唐秋凡, 付小龙. 含能黏合剂3-硝酸酯甲基-3-甲基氧丁环聚合物的固化体系研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(8): 1401-1408. |
| [13] | 何伟, 何利明, 马中亮, 肖忠良, 郭彦丽. 利用流变学等温测试方法研究铝对聚叠氮缩水甘油醚改性球形药固化的影响[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(6): 1023-1029. |
| [14] | 王传华, 郭晓燕, 邹美帅, 杨荣杰. 铝基水反应活性材料制备及其性能研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(5): 817-822. |
| [15] | 杨后文, 余永刚, 叶锐. 不同火焰环境下固体火箭发动机烤燃特性数值模拟[J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(9): 1640-1646. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4
京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4