


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (10): 250442-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2025.0442
Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Hao1, XU Peng1, CHEN De2,*( )
)
Received:2025-06-03
Online:2025-11-05
Contact:
CHEN De
WU Hao, XU Peng, CHEN De. Design of Compressed Air-drivenVariable-sectional Shock Tube for Simulating Air Explosion Shock Wave[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(10): 250442-.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
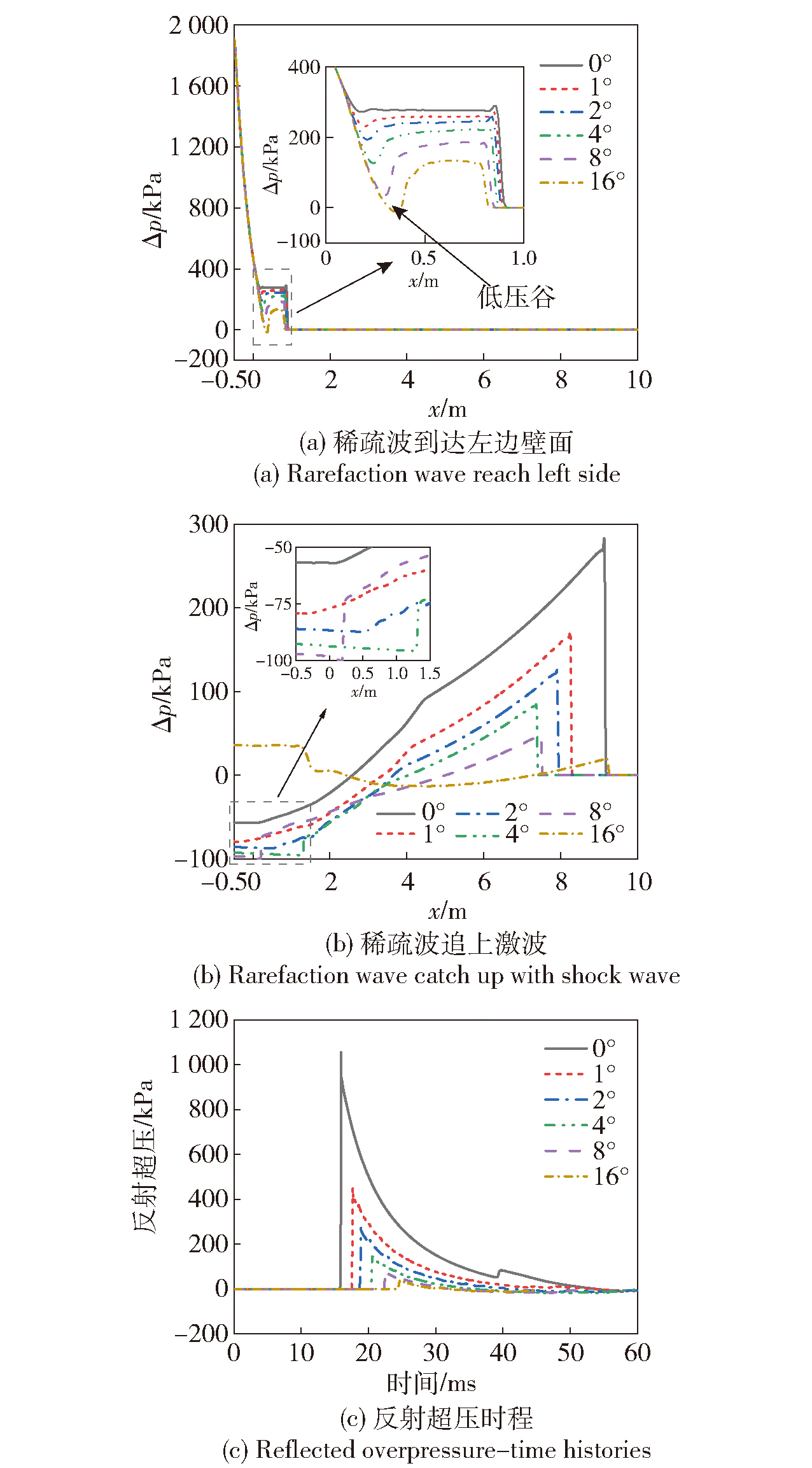
Fig.14 Instantaneous pressure distribution inside the variable-sectional shock tube with different expanded angle and corresponding reflected overpressure-time histories
| 激波管 | D/m | θ/(°) | S/m | L/m | Dend/m | p4/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.5 | 9 | 8.5 | 0.55 | 3 | 2 |
| B | 0.5 | 11 | 7 | 0.5 | 3 | 5 |
| C | 0.5 | 7 | 7 | 0.51 | 2 | 5 |
Table 1 Variable-sectional shock tube design parameters
| 激波管 | D/m | θ/(°) | S/m | L/m | Dend/m | p4/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.5 | 9 | 8.5 | 0.55 | 3 | 2 |
| B | 0.5 | 11 | 7 | 0.5 | 3 | 5 |
| C | 0.5 | 7 | 7 | 0.51 | 2 | 5 |
| 激波管 | 式(10)预测Δpr/kPa | 数值仿真Δpr/kPa | 相对误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 107.8 | 103.4 | 4.2 |
| B | 202.5 | 200.8 | 0.84 |
| C | 329.6 | 312.2 | 5.6 |
Table 2 Comparison of numerical simulation analysis results and Eq. (10) predictions
| 激波管 | 式(10)预测Δpr/kPa | 数值仿真Δpr/kPa | 相对误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 107.8 | 103.4 | 4.2 |
| B | 202.5 | 200.8 | 0.84 |
| C | 329.6 | 312.2 | 5.6 |
| 激波管 类型 | 激波管冲击波 | 空爆冲击波 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p4/MPa | Δpr/kPa | Δt+/ms | b | 爆炸当量/kg | 爆炸距离/m | Δp'r[ | T+[ | b'[ | |
| 0.5 | 36.4 | 6.2 | 0.55 | 4 | 12 | 34.8 | 6.1 | 0.47 | |
| A | 1 | 63.2 | 7.6 | 0.93 | 12 | 12 | 64.1 | 7.8 | 0.73 |
| 1.5 | 84.5 | 9.6 | 1.47 | 30 | 14 | 85.9 | 10.0 | 0.87 | |
| 2 | 103.4 | 10.1 | 1.43 | 40 | 14 | 104.8 | 10.6 | 0.98 | |
| 1 | 63.9 | 6.8 | 0.92 | 9 | 11 | 63.1 | 7.1 | 0.72 | |
| 2 | 105.9 | 9.0 | 1.52 | 25 | 12 | 104.2 | 9.0 | 0.97 | |
| B | 3 | 141.0 | 9.9 | 1.58 | 40 | 12 | 147.7 | 9.9 | 1.17 |
| 4 | 172.3 | 10.4 | 1.55 | 50 | 12 | 176.1 | 10.3 | 1.28 | |
| 5 | 200.8 | 11.0 | 1.6 | 75 | 13 | 201.5 | 11.5 | 1.37 | |
| 1 | 100.3 | 7.7 | 1.59 | 14 | 10 | 101.8 | 7.5 | 0.96 | |
| 2 | 167.3 | 9.6 | 1.87 | 35 | 11 | 163.2 | 9.3 | 1.23 | |
| C | 3 | 222.4 | 11.9 | 2.36 | 85 | 13 | 223.6 | 11.8 | 1.44 |
| 4 | 270.3 | 14.9 | 3.02 | 200 | 16 | 272.7 | 14.9 | 1.58 | |
| 5 | 312.2 | 16.8 | 2.57 | 280 | 17 | 312.2 | 16.0 | 1.68 | |
Table 3 Mapping relationship of reflected overpressure parameters of shock tubes and air explosion shock waves
| 激波管 类型 | 激波管冲击波 | 空爆冲击波 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p4/MPa | Δpr/kPa | Δt+/ms | b | 爆炸当量/kg | 爆炸距离/m | Δp'r[ | T+[ | b'[ | |
| 0.5 | 36.4 | 6.2 | 0.55 | 4 | 12 | 34.8 | 6.1 | 0.47 | |
| A | 1 | 63.2 | 7.6 | 0.93 | 12 | 12 | 64.1 | 7.8 | 0.73 |
| 1.5 | 84.5 | 9.6 | 1.47 | 30 | 14 | 85.9 | 10.0 | 0.87 | |
| 2 | 103.4 | 10.1 | 1.43 | 40 | 14 | 104.8 | 10.6 | 0.98 | |
| 1 | 63.9 | 6.8 | 0.92 | 9 | 11 | 63.1 | 7.1 | 0.72 | |
| 2 | 105.9 | 9.0 | 1.52 | 25 | 12 | 104.2 | 9.0 | 0.97 | |
| B | 3 | 141.0 | 9.9 | 1.58 | 40 | 12 | 147.7 | 9.9 | 1.17 |
| 4 | 172.3 | 10.4 | 1.55 | 50 | 12 | 176.1 | 10.3 | 1.28 | |
| 5 | 200.8 | 11.0 | 1.6 | 75 | 13 | 201.5 | 11.5 | 1.37 | |
| 1 | 100.3 | 7.7 | 1.59 | 14 | 10 | 101.8 | 7.5 | 0.96 | |
| 2 | 167.3 | 9.6 | 1.87 | 35 | 11 | 163.2 | 9.3 | 1.23 | |
| C | 3 | 222.4 | 11.9 | 2.36 | 85 | 13 | 223.6 | 11.8 | 1.44 |
| 4 | 270.3 | 14.9 | 3.02 | 200 | 16 | 272.7 | 14.9 | 1.58 | |
| 5 | 312.2 | 16.8 | 2.57 | 280 | 17 | 312.2 | 16.0 | 1.68 | |
| [3] |
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0260 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1177/2041419619858098 URL |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104004 URL |
| [8] |
陈德, 吴昊, 徐世林, 等. 单向砌体填充墙激波管试验和动力行为分析[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(8): 136-154.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
杨军, 薛斌. 激波管管长对阶跃压力波形的影响分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(3): 252-257.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2023.11.026 URL |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2021.02.029 URL |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2024.104894 URL |
| [3] |
刘钰, 鲁殊凡, 索涛, 等. 充液管结构人员抗爆炸冲击防护试验研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(7): 2374-2382.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0260 |
| [11] |
周岳兰, 裴鲁, 龙仁荣, 等. 激波管内压力脉冲演化特性及模拟空爆冲击波的方法研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(12): 3815-3825.
doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0284 |
|
|
|
| [12] |
张仕忠, 李进平, 康越, 等. 激波管模拟产生近场爆炸冲击波[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(12): 137-148.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
何起光. 激波管冲击载荷作用下预制孔铝板的响应特性研究[D]. 黑龙江: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/0045-7825(74)90029-2 URL |
| [16] |
ANSYS. Ansys fluent theory guide[M]. Europe: Ansys Europe ltd, 2023.
|
| [17] |
戴嘉宁, 辜峙钘, 张玲, 等. 基于EOS压力迭代的压力波传播CFD模型研究[J]. 核科学与工程, 2023, 43(2): 278-285.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
潘沙, 丁国昊, 王文龙, 等. 一维激波管问题差分格式计算对比分析[C]// 中国力学学会激波与激波管专业委员会. 第十三届全国激波与激波管学术会议论文集. 长沙: 国防科技大学航天与材料工程学院, 2008: 162-171.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
UNODA. International ammunition technical guideline(IATG 01.80)[R]. New York: United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs, 2015.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [1] | AN Chengyuan, LIU Haipeng, LIU Yan, REN Wei. Shock Wave Power Characteristics of Cylindrical Explosives with Elliptical Cross-section [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(8): 240969-. |
| [2] | LIU Gangwei, ZHANG Jingyuan, SHI Zhangsong, TAN Bo, SONG Pu, HU Hongwei, LU Yongjin. Effect of Shock Wave Load in Underwater Explosion of Cased Charge near Seabed [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(8): 240643-. |
| [3] | WANG Ran, ZHANG Yiming, GUO Songlin, WANG Haosen, WANG Ningfei, WU Yi. Dynamic Response and Damage Evolution of Cracked Composite Solid Propellants under Shock Wave Loading [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(7): 240778-. |
| [4] | MA Dong, WANG Cheng, SHAO Nan, WEI Jianshu. Strengthening Effect of Polyurea on Multi-layer Blast-resistant Structure Subjected to Combined Action of Shock Wave and Fragments [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(7): 240798-. |
| [5] | ZHA Jipeng, ZHANG Xiangjin, HUA Tuan, SHENG Na, KANG Yang. Analysis of the Influence of Shock Waves on the Detection Performance of Laser Fuze under High-speed Flight Conditions [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(6): 241131-. |
| [6] | LIU Zheng, NIE Jianxin, KAN Runzhe, YANG Jinxiang, TAN Yanwei, GUO Xueyong, YAN Shi. Effect of Aluminum Powder Combustion on the Underwater Explosion Load Characteristics of CL-20-based Mixed Explosives [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(3): 240128-. |
| [7] | XIAO Zeqi, GAO Xin, ZHANG Xueying, LIU Kaiyuan, YUE Lidan, QIN Zhiqi, CHEN Pengwan. Explosive Shock Synthesis of Cesium Lead Chloride Perovskite Powder [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(3): 240339-. |
| [8] | ZHANG Fenglin, DONG Yihao, XIN Jianshe, GUO Liping, GU Xuechen, QU Jiaqi. Parameter Selection and Optimization Algorithm for Low-overload Compressed Air Launch of Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Based on Particle Swarm Optimization [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(2): 240014-. |
| [9] | LI Gang, HU Zhongling, HU Bin, LI Zhiyu, CAI Meng, HUANG Tushun. Dynamic Response Characteristics of Human Ear Subjected to High-intensity Sound Shock Wave [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(1): 231119-. |
| [10] | JIA Shiyu, WANG Cheng, XU Wenlong, MA Dong, QI Fangfang. Protective Performance of Helmet with Annular Composite Liner [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(1): 231220-. |
| [11] | WANG Tao, LIU Liangtao, WANG Jinxiang, ZHANG Yifan. The Damage Characteristics of Underwater Explosion of Explosives with Different Energy Structures on the Side Multi-cabin Structure [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(1): 231201-. |
| [12] | LI Yin, DENG Guoqiang. Study on the Assessment of Damage level of Explosion Damage Elements against Personnel [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(S2): 186-192. |
| [13] | YU Jiaxin, LI Weibing, LI Junbao, BI Weixin, LUO Yusong. The Influence of Multi-layer Explosion-proof Structure on the Energy Output of Power Controllable Warhead [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(S1): 33-42. |
| [14] | JIANG Xinli, ZHANG Guokai, HE Yong, YAO Jian, WANG Zhen, WU Yuxin, LIU Ju, WANG Mingyang. Afterburning Effect of Thermobaric Explosives in Confined Space [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(8): 2520-2530. |
| [15] | LIU Yu, LU Shufan, SUO Tao, HOU Bing, FAN Zhiqiang, LI Yuan. Experimental Study on the Effect of Liquid-filled Tube Structure on Shock Wave Attenuation [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(7): 2374-2382. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||