


Responsible Institution: China Association for Science and Technology
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
Sponsor: China Ordnance Society
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



Acta Armamentarii ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (10): 250200-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2025.0200
Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yunlong, ZHAO Zhengyuan, WU Zhilin*( ), LI Zhongxin**(
), LI Zhongxin**( )
)
Received:2025-03-21
Online:2025-11-05
Contact:
WU Zhilin, LI Zhongxin
WANG Yunlong, ZHAO Zhengyuan, WU Zhilin, LI Zhongxin. Mechanical Characteristics and Firing Disturbance of a Lightweight Remote-Controlled Weapon Station Under Multi-Condition Operations[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(10): 250200-.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
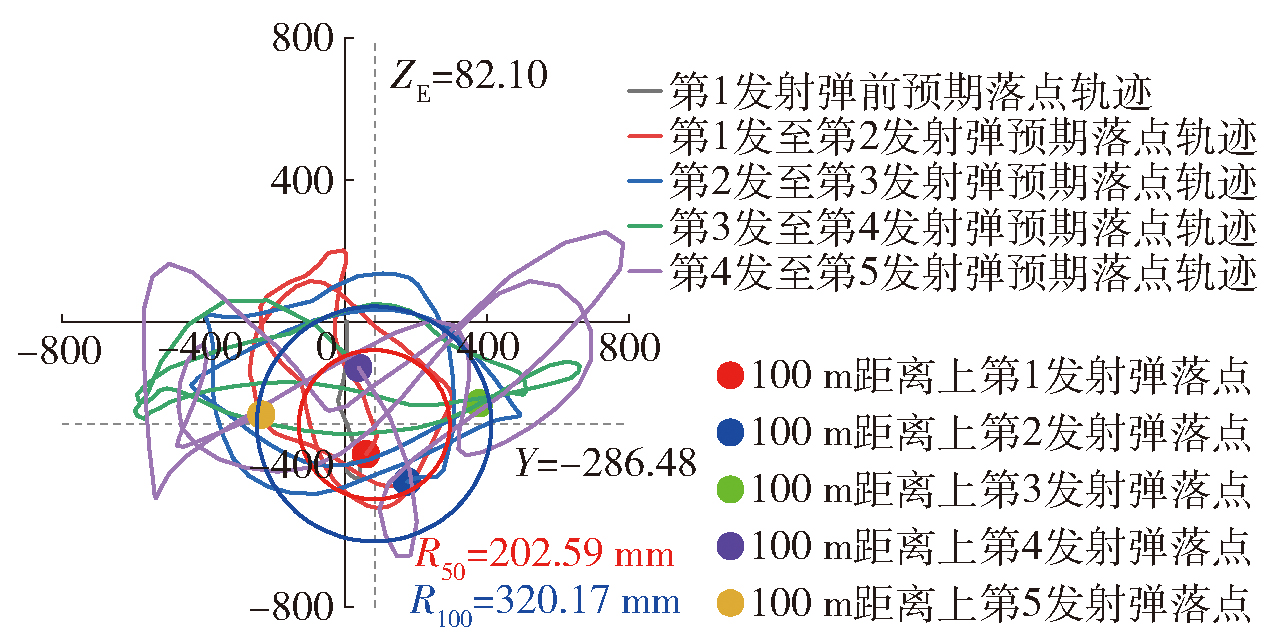
Fig.18 Schematic diagram of the impact effect of a remote-controlled weapon station on a target at 100m under continuous shooting conditions after adding a buffer
| 组数 | 刚性连接 | 柔性连接 | 组数 | 刚性连接 | 柔性连接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 476.67 | 216.47 | 7 | 645.24 | 320.10 |
| 2 | 441.41 | 170.07 | 8 | 471.07 | 338.00 |
| 3 | 301.98 | 256.86 | 9 | 381.78 | 163.37 |
| 4 | 465.65 | 228.91 | 10 | 448.87 | 301.99 |
| 5 | 659.59 | 265.24 | 均值 | 458.14 | 248.12 |
| 6 | 289.13 | 220.21 |
Table 1 Statistical results of shooting test mm
| 组数 | 刚性连接 | 柔性连接 | 组数 | 刚性连接 | 柔性连接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 476.67 | 216.47 | 7 | 645.24 | 320.10 |
| 2 | 441.41 | 170.07 | 8 | 471.07 | 338.00 |
| 3 | 301.98 | 256.86 | 9 | 381.78 | 163.37 |
| 4 | 465.65 | 228.91 | 10 | 448.87 | 301.99 |
| 5 | 659.59 | 265.24 | 均值 | 458.14 | 248.12 |
| 6 | 289.13 | 220.21 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
郑博文, 毛保全, 钟孟春, 等. 智能武器站发展现状与关键技术分析[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(5): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
史婷娜, 谭本慷, 徐奕扬, 等. 机器人关节伺服系统力矩控制技术综述[J/OL]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025: 1-18. [2025-03-08]. https://doi.org/10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.241599.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
吴永亮, 毛保全, 高玉水, 等. 遥控武器站研究现状与发展[J]. 高技术通讯, 2014, 24(2): 193-200.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1177/09544070241232730 URL |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2023.12.012 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1007/s12206-023-1133-y |
| [9] |
刘强, 周克栋, 宋伟, 等. 某埋头弹机枪退壳系统设计与动力学分析[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 1265-1273.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
何龙, 姜荃, 李鹏杰, 等. 穿戴武器臂的人枪耦合系统发射响应研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 386-394.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
谢馨, 张连超, 郑杰基, 等. 路面不平度对遥控武器站伺服性能的影响分析[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2024, 54(6): 1137-1148.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1177/09544062221115106 URL |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2024.04.011 URL |
| [14] |
doi: 10.14429/dsj.72.17040 URL |
| [15] |
朱锐, 毛保全, 赵俊严, 等. 机枪遥控武器站锰铜基阻尼合金缓冲器非线性有限元分析及试验[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 935-946.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
陆星宇, 曹岩枫, 庄圆, 等. 四足打击平台多工况力学特性及射击扰动[J]. 工程科学学报, 2024, 46(8): 1434-1445.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
杨沫, 赫雷, 周克栋, 等. 某专用枪械后坐缓冲装置设计与分析[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2025(6): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
冯帅, 毛保全, 王之千, 等. 基于自适应混合近似模型的顶置武器站多柔体系统动力学优化研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(12): 206-212.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
孙章毅, 蔡灿伟. 动载荷作用下迫击炮与土壤刚柔耦合响应分析[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2023, 45(1): 102-107.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2023.01.017 |
|
|
|
| [20] |
张雅斌, 刘宁, 黄建文, 等. 迫击炮协调臂前装填系统动力学仿真[J]. 火炮发射与控制学报, 2025, 46(2):83-88,96.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
华洪良, 廖振强, 郭魂, 等. 机枪系统支撑发射动力学特性及散布精度研究[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(1): 42-47.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
曾鑫, 先苏杰, 许德鹏, 等. 某埋头弹机枪自动机结构设计与动力学分析[J]. 兵工自动化, 2021, 40(3): 26-28, 39.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
张小石, 王宪升, 喻翔, 等. 某自动步枪机构动力学仿真分析[J]. 机械工程与自动化, 2021(4): 64-66,69.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
欧天界, 贾陆阳, 李东昊, 等. 某导气式自动武器动力学仿真及试验[J]. 兵工自动化, 2024, 43(11): 57-60, 86.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
吴迪, 顾祖成, 王永娟, 等. 某小型无人化作战平台机电联合仿真[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2020, 41(5): 86-90.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
司鹏, 王云龙, 宋杰, 等. 中口径枪弹全弹道建模及弹道特征量分析[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2025, 46(7): 37-43.
|
|
|
| [1] | LIU Kun, FENG Ying, KANG Bao, WU Zhilin, SONG Jie, ZHU Tao. Study on the Shooting Vibration Characteristics of a Quadruped Unmanned Combat Platform under Impact Loads [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(10): 250282-. |
| [2] | LIU Taisu, YIN Qiang, LI Yong, ZHANG Yuntian. Rigid-flexible Coupling Dynamic Modeling and Characteristics Analysis of a Rotational Chain Magazine [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(11): 4133-4144. |
| [3] | CAI Yunlong, YANG Lina, QUAN Liang, YANG Baosheng, REN Ruoyu. Design and Optimization of Locust-hindfoot-inspired Embedded Missile Ejection Device [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(11): 3983-3997. |
| [4] | MU Lindong, ZHAO Xinlei, XU Peng, QIU Tianqi, JIANG Lei. Two-wheeled Power-assist Trailer Payload Based on Force Control [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(S2): 61-70. |
| [5] | GAO Pu, LI Hongcai, LIU Hui, MENG Jieke. Analysis on Dynamic Characteristics of External Oil Pipe System of Integrated Transmission Device in Armoured Vehicle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(11): 3447-3454. |
| [6] | RONG Ji-li, XIN Peng-fei, ZHUGE Xun, YANG Yong-tai, XIANG Da-lin. Capturing Dynamics of Flexible Ropes for Space Large-scale End Effector [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(9): 1730-1737. |
| [7] | ZHEN Wen-qiang, JI Yong-qiang, SHI Yun-guo. Dynamic Simulation and Experimental Study of Deployment Process of Missile Folding-wing [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(8): 1409-1414. |
| [8] | LYU Xiao-chen, LI Guo-xiu, SUN Zuo-yu, GAO Qing-xiu , WANG Jie, HE Shuang-yi, CUI Sui-xian. Effect of High Pressure Fuel Pipe Structure on Performance of Electronic Unit Pump Fuel System [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(10): 1778-1787. |
| [9] | HU Sheng-hai, GUO Chun-yang, YU Wei, QI Song, SUN Jun-chao. Rigid-flexible Coupling Dynamic Modeling and Error Analysis of Loading Mechanism of Naval Gun Based on MetamorphicPrinciple [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(8): 1398-1404. |
| [10] | HUA Hong-liang, LIAO Zhen-qiang, SONG Jie, QIU Ming, XIAO Jun-bo. The Application of Reverse Jet Gas Technology in Improving Firing Accuracy of a Machine Gun System [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(12): 2241-2246. |
| [11] | LI Jia-sheng, QIU Ming, LIAO Zhen-qiang, XIAN Dong-peng, SONG Jie. Dynamic Modeling and Simulation of Gatling Gun with Muzzle Assistant-Rotating and Recoil Absorber [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(9): 1344-1349. |
| [12] | HU Kai-ming, WEN Li-hua, YAN Zhao-qi. Static and Dynamic Simulation and Analysis on PBP Actuator with a Connecting rod Mechanism to MagnifyOutput Angular Displacement [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(8): 1258-1266. |
| [13] | HUANG Xue-tao, GU Liang, LYU Wei-wei, YANG Cong-bin, GAO Xiao-dong, ZHU Xing-gao. Track Tension and Its Influencing Factors [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(7): 1110-1118. |
| [14] | FAN Bao-wei, PAN Jian-feng , CHEN Rui, LIU Yang-xian, TANG Ai-kun, WANG Qian. Effect of Ignition Advance Angles on Combustion Process in Natural Gas-fueled Rotary Engine [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(1): 1-8. |
| [15] | REN Kai, YANG Li, PU Jin-yun, SU Xue-rong. An Interactive Virtual Compartment Fire Extinguishing Model Based on System Dynamic Characteristic [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2013, 34(9): 1137-1143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||