


主管单位:中国科学技术协会
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



兵工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (S1): 250635-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2025.0635
收稿日期:2025-07-13
上线日期:2025-11-06
通讯作者:
ZHANG Mohe1,2, PANG Siping1,*( )
)
Received:2025-07-13
Online:2025-11-06
摘要:
为寻找可低成本处理含有三硝基甲苯(2,4,6-trinitrotoluene,TNT)废水的吸附材料,采用褐煤制备的活性焦(Activited Coke,AC)吸附含有TNT的废水,分析动力学和热力学规律、吸附前后AC表面和热重差热变化,结果表明:AC吸附TNT的动力学符合拟二级动力学模型,颗粒内扩散是其限速步骤,吸附过程是一个吸热过程、以化学吸附为主;Redlich-Peterson吸附等温线模型更适合拟合AC吸附TNT的过程;当TNT浓度为98.8mg/L,AC浓度为2.5g/L,pH为中性,温度为40℃,振荡时间为360min时,TNT去除率可达99.4%;吸附TNT前后AC的表面孔隙被堵塞,热解峰温从546.5℃降低至521.5℃、热流量从178.5mW增大至209.6mW。
张默贺, 庞思平. 活性焦吸附TNT废水[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(S1): 250635-.
ZHANG Mohe, PANG Siping. Study on the Adsorption of TNT Wastewater by Activated Coke[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(S1): 250635-.
| 物理特性 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 414.3247 |
| 总孔隙体积/(m3·g-1) | 0.266118 |
| 平均孔径/nm | 2.6059 |
| 堆积密度/(g·cm-3) | 0.55 |
| 显性密度/(g·cm-3) | 0.39 |
| 在氮气实际压力和饱和蒸汽压力的比值条件下直径小于363.8383nm的孔的单点总孔径 | 0.99467422 |
| 化学特性 | 质量百分比/% |
| C | 76.77 |
| H | 1.02 |
| N | 0.66 |
| Ash | 21.55 |
表1 AC的物理化学特性
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of AC
| 物理特性 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 414.3247 |
| 总孔隙体积/(m3·g-1) | 0.266118 |
| 平均孔径/nm | 2.6059 |
| 堆积密度/(g·cm-3) | 0.55 |
| 显性密度/(g·cm-3) | 0.39 |
| 在氮气实际压力和饱和蒸汽压力的比值条件下直径小于363.8383nm的孔的单点总孔径 | 0.99467422 |
| 化学特性 | 质量百分比/% |
| C | 76.77 |
| H | 1.02 |
| N | 0.66 |
| Ash | 21.55 |
| T / ℃ | qe/ (mg· g-1) | 拟一级动力学 | 拟二级动力学 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q1/ (mg· g-1) | k1/ (min-1) | | q2/ (mg· g-1) | k2/(g· mg-1· min-1) | h/ (mg· g-1· min-1) | | ||
| 20 | 40.9 | 30.8 | 9.86×10-3 | 0.991 | 44.2 | 5.76×10-4 | 1.13 | 0.996 |
| 30 | 41.3 | 26.6 | 9.72×10-3 | 0.967 | 44.1 | 6.16×10-4 | 1.42 | 0.998 |
| 40 | 44.8 | 31.3 | 1.04×10-2 | 0.990 | 47.9 | 6.72×10-4 | 1.47 | 0.997 |
表2 AC吸附TNT的吸附动力学参数
Table 2 Kinetics parameters for the adsorption of TNT by AC
| T / ℃ | qe/ (mg· g-1) | 拟一级动力学 | 拟二级动力学 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q1/ (mg· g-1) | k1/ (min-1) | | q2/ (mg· g-1) | k2/(g· mg-1· min-1) | h/ (mg· g-1· min-1) | | ||
| 20 | 40.9 | 30.8 | 9.86×10-3 | 0.991 | 44.2 | 5.76×10-4 | 1.13 | 0.996 |
| 30 | 41.3 | 26.6 | 9.72×10-3 | 0.967 | 44.1 | 6.16×10-4 | 1.42 | 0.998 |
| 40 | 44.8 | 31.3 | 1.04×10-2 | 0.990 | 47.9 | 6.72×10-4 | 1.47 | 0.997 |
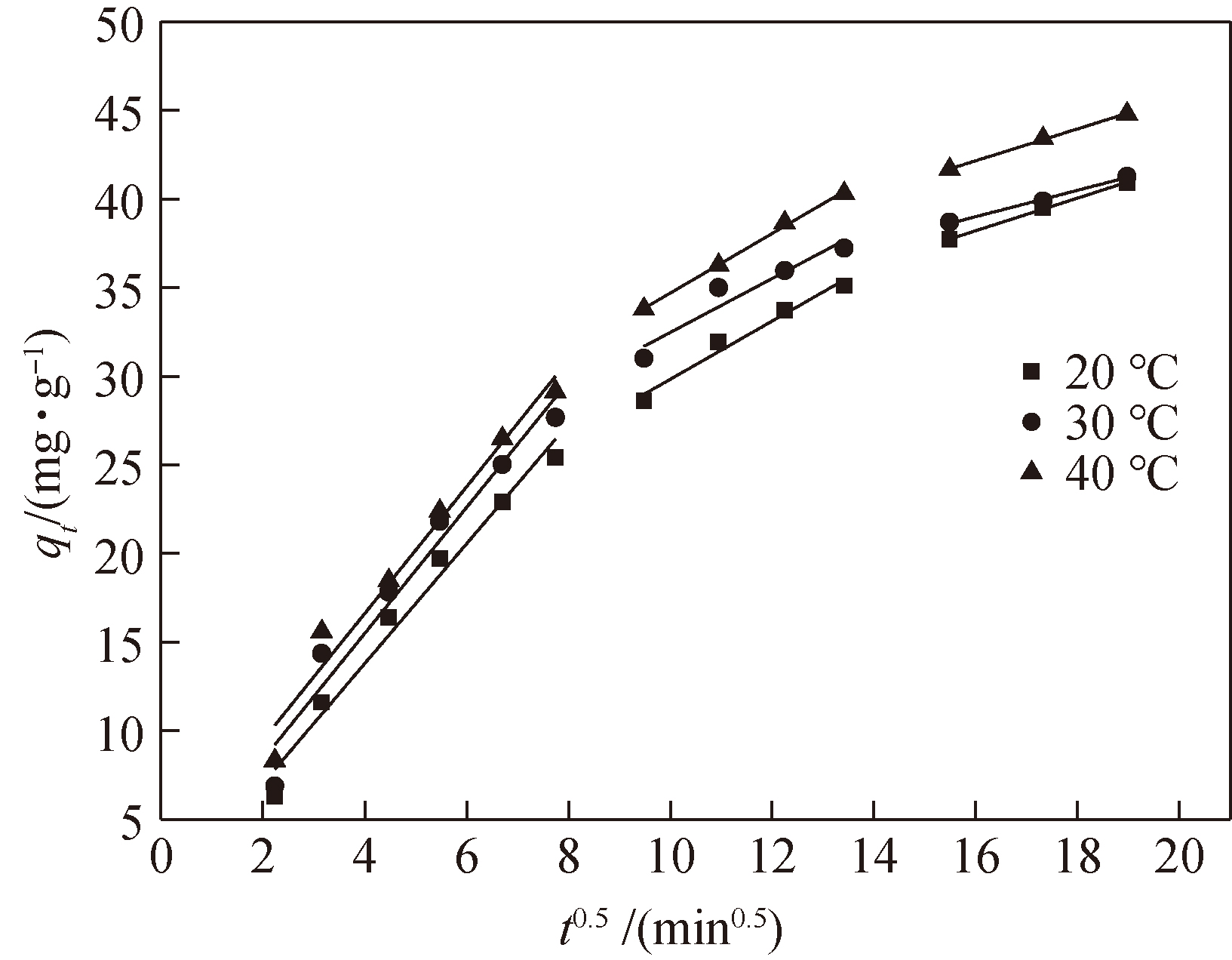
图7 qt随t0.5的变化的颗粒内扩散曲线(pH值:7;温度:40℃;TNT初始浓度:87.5mg/L;AC质量:1.5g/L)
Fig.7 Intraparticle diffusion plot for qt and t0.5 (pH:7; T:40℃;initial concentration of TNT:87.5mg/L; AC dosage:1.5g/L)
| T/ ℃ | Langmuir 吸附模型 | Freundlich 吸附模型 | Redlich-Peterson 吸附模型 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/ (mg· g-1) | Ka/ (L· mg-1) | | KF | n | | A/ (L· mg-1)g | B/ (L· g-1) | g | | |
| 20 | 59.5 | 6.03 ×10-2 | 0.997 | 13.5 | 3.28 | 0.994 | 12.5 | -0.421 | 0.764 | 0.999 |
| 30 | 53.3 | 1.27 ×10-1 | 0.989 | 23.3 | 5.79 | 0.849 | 21.7 | -0.324 | 0.880 | 0.994 |
| 40 | 69.5 | 5.97 ×10-2 | 0.965 | 15.5 | 3.25 | 0.903 | 40.6 | -0.835 | 0.718 | 0.984 |
表3 AC吸附TNT的等温曲线参数
Table 3 Isotherm parameters for the adsorption of TNT onto AC
| T/ ℃ | Langmuir 吸附模型 | Freundlich 吸附模型 | Redlich-Peterson 吸附模型 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/ (mg· g-1) | Ka/ (L· mg-1) | | KF | n | | A/ (L· mg-1)g | B/ (L· g-1) | g | | |
| 20 | 59.5 | 6.03 ×10-2 | 0.997 | 13.5 | 3.28 | 0.994 | 12.5 | -0.421 | 0.764 | 0.999 |
| 30 | 53.3 | 1.27 ×10-1 | 0.989 | 23.3 | 5.79 | 0.849 | 21.7 | -0.324 | 0.880 | 0.994 |
| 40 | 69.5 | 5.97 ×10-2 | 0.965 | 15.5 | 3.25 | 0.903 | 40.6 | -0.835 | 0.718 | 0.984 |
| 状态 | C | N | H |
|---|---|---|---|
| 吸附前AC | 76.77 | 0.66 | 1.02 |
| 吸附后AC | 71.53 | 1.53 | 1.03 |
表4 吸附前后的AC表面的元素重量比
Table 4 The element weight of AC before and after adsorption %
| 状态 | C | N | H |
|---|---|---|---|
| 吸附前AC | 76.77 | 0.66 | 1.02 |
| 吸附后AC | 71.53 | 1.53 | 1.03 |
| 吸附量/ (mg(TNT)·g-1) | 吸附剂价格/ (元·g-1) | 效费比/ (mg(TNT)·元-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 椰壳活性炭 | 161.3 | 0.003 | 5.37×104 |
| 木质素活性炭 | 55.7 | 0.0015 | 3.71×104 |
| AC | 58.3 | 0.0005 | 1.17×105 |
表5 不同吸附剂吸附TNT 的对比分析
Table 5 Comparison of different adsorbents adsorbing TNT
| 吸附量/ (mg(TNT)·g-1) | 吸附剂价格/ (元·g-1) | 效费比/ (mg(TNT)·元-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 椰壳活性炭 | 161.3 | 0.003 | 5.37×104 |
| 木质素活性炭 | 55.7 | 0.0015 | 3.71×104 |
| AC | 58.3 | 0.0005 | 1.17×105 |
| [1] |
pmid: 11566402 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55573-w pmid: 38413693 |
| [5] |
pmid: 17980428 |
| [6] |
pmid: 15629570 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55573-w pmid: 38413693 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.04.055 pmid: 19446826 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4
京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4