


主管单位:中国科学技术协会
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ
主办单位:中国兵工学会
ISSN 1000-1093 CN 11-2176/TJ



兵工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (S1): 250491-.doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2025.0491
收稿日期:2025-06-12
上线日期:2025-11-06
通讯作者:
CHEN Shuang, WU Benxiang*( ), CHEN Cheng
), CHEN Cheng
Received:2025-06-12
Online:2025-11-06
摘要:
随着船舶电力系统不断发展,中性点经高阻接地的中压电力系统正在被广泛应用,单相断线故障作为常见电气故障,将给系统带来较高的过电压。针对该系统单相断线故障的3种情况进行分析,分别为断线不接地、断线点电源侧接地及断线点负荷侧接地,综合考虑接地点过渡电阻、负荷阻抗、断线位置等要素,采用对称相量法推导出断口前后零序电压解析表达式;基于反演变换和共形映射理论,分析了不同情况下两端过电压的关系特征;搭建典型电力系统仿真模型,验证了理论分析结果的正确性,为今后实现系统单相断线故障的精确定位提供理论支撑。
陈爽, 吴本祥, 陈诚. 中性点经高阻接地的船舶中压交流电力系统单相断线故障特性[J]. 兵工学报, 2025, 46(S1): 250491-.
CHEN Shuang, WU Benxiang, CHEN Cheng. Research on the Fault Characteristics of Single-phase Broken Conductor in High-resistance Grounded Marine MV AC Power Systems[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2025, 46(S1): 250491-.
| 线路 类型 | R1/ (Ω·km-1) | C1/ (F·km-1) | L1/ (mH·km-1) | R0/ (Ω·km-1) | C0/ (F·km-1) | L0/ (mH·km-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电缆 | 0.12 | 0.15×10-6 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.9×10-6 | 0.65 |
表1 仿真模型中电缆设置参数
Table 1 Cable setting parameters in the simulation model
| 线路 类型 | R1/ (Ω·km-1) | C1/ (F·km-1) | L1/ (mH·km-1) | R0/ (Ω·km-1) | C0/ (F·km-1) | L0/ (mH·km-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电缆 | 0.12 | 0.15×10-6 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.9×10-6 | 0.65 |
| 断线不接地 | 断线点电源侧接地 | 断线点负载侧接地 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL/Ω | | | | | | |
| 50 | 11.4 | 2714.0 | 1795.7 | 4456.7 | 57.9 | 1796.0 |
| 100 | 22.8 | 2713.0 | 2693.0 | 5353.3 | 113.3 | 1758.3 |
| 200 | 45.4 | 2710.0 | 3590.0 | 6250.0 | 216.9 | 1687.7 |
| 300 | 67.8 | 2705.3 | 4036.7 | 6696.7 | 311.9 | 1623.0 |
| 400 | 89.8 | 2699.0 | 4306.7 | 6966.7 | 399.0 | 1563.7 |
| 500 | 111.4 | 2691.0 | 4486.7 | 7143.3 | 479.0 | 1509.7 |
| 1000 | 209.5 | 2635.3 | 4893.3 | 7553.3 | 792.3 | 1304.0 |
| 1500 | 288.0 | 2566.0 | 5046.7 | 7703.3 | 1008.3 | 1175.3 |
| 2000 | 347.0 | 2498.3 | 5126.7 | 7783.3 | 1161.0 | 1095.7 |
| 2500 | 390.3 | 2439.7 | 5176.7 | 7833.3 | 1275.0 | 1045.0 |
| 3000 | 421.7 | 2391.7 | 5210.0 | 7866.7 | 1368.7 | 1014.3 |
表2 α=1/2时3种断线故障类型仿真结果(部分)
Table 2 Simulated results of three types of disconnection faults (part) for α=1/2
| 断线不接地 | 断线点电源侧接地 | 断线点负载侧接地 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL/Ω | | | | | | |
| 50 | 11.4 | 2714.0 | 1795.7 | 4456.7 | 57.9 | 1796.0 |
| 100 | 22.8 | 2713.0 | 2693.0 | 5353.3 | 113.3 | 1758.3 |
| 200 | 45.4 | 2710.0 | 3590.0 | 6250.0 | 216.9 | 1687.7 |
| 300 | 67.8 | 2705.3 | 4036.7 | 6696.7 | 311.9 | 1623.0 |
| 400 | 89.8 | 2699.0 | 4306.7 | 6966.7 | 399.0 | 1563.7 |
| 500 | 111.4 | 2691.0 | 4486.7 | 7143.3 | 479.0 | 1509.7 |
| 1000 | 209.5 | 2635.3 | 4893.3 | 7553.3 | 792.3 | 1304.0 |
| 1500 | 288.0 | 2566.0 | 5046.7 | 7703.3 | 1008.3 | 1175.3 |
| 2000 | 347.0 | 2498.3 | 5126.7 | 7783.3 | 1161.0 | 1095.7 |
| 2500 | 390.3 | 2439.7 | 5176.7 | 7833.3 | 1275.0 | 1045.0 |
| 3000 | 421.7 | 2391.7 | 5210.0 | 7866.7 | 1368.7 | 1014.3 |
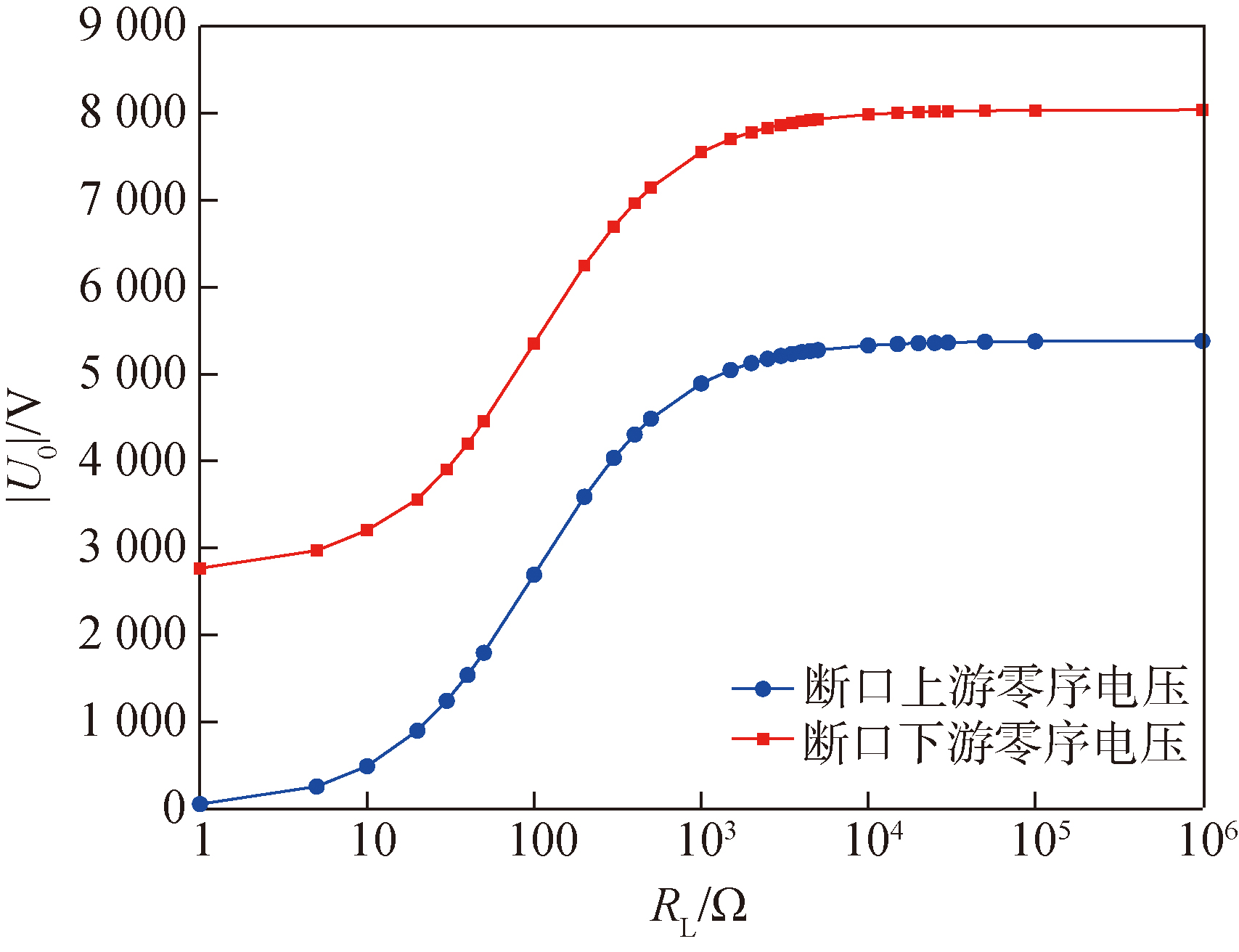
图20 α=1/2时断线点电源侧接地故障零序电压特性曲线
Fig.20 Zero-sequence voltage characteristic curve of power supply side grounding fault at the disconnection point when α=1/2
| [1] |
王燕. 船舶中压电力系统中性点接地与过电压研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2011.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
罗宁昭, 张晓锋, 杨锋. 舰船中压电力系统接地方式研究[J]. 船海工程, 2011, 40(5):118-120,124.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
张弛. 10kV电力系统单相断线故障特征分析与定位方法[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2022.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
张慧芬, 潘贞存, 桑在中. 中性点电阻接地系统单相断线加接地故障的分析[J]. 继电器, 2004(18):6-9.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
张林利, 曹丽丽, 李立生, 等. 不接地系统单相断线故障分析及区段定位[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(16):1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
王鹏玮, 徐丙垠, 王超, 等. 基于故障相电压与零序电流相位比较的中性点不接地系统高阻接地故障保护方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44(10):148-156.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
唐钊. 不接地系统单相断线故障负序电流分析[J]. 电工技术, 2024(9):68-70.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
周斌, 陈梦琦, 郑海涯, 等. 谐振接地系统单相断线并坠地故障电压特征仿真分析[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(17):93-100.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
何东, 甘贝贝, 袁英硕, 等. 基于限流电抗器暂态电压余弦相似度的直流配电网纵联保护方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18(12):1-9,18.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
薛永端, 李娟, 徐丙垠. 中性点经消弧线圈接地系统小电流接地故障暂态等值电路及暂态分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(22):5703-5714.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
田君杨, 李海勇, 蒋连钿, 等. 含多分布式电源的小电阻接地系统单相接地故障特征分析[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52(14):103-110.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
陈俊梁. 基于继电保护与配电自动化的10kV配电线路故障处理分析[J]. 电工技术, 2024(增刊2):692-695.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
张浩, 张大海, 刘乃毓, 等. 基于改进VMD及ConvNeXt的小电流接地系统单相接地故障选线方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2025, 51(2):730-741.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
朱玲玲, 张华中, 王正刚, 等. 基于小波神经网络单相断线故障选线和定位[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2011, 39(4):12-17.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
常仲学, 宋国兵, 张维. 配电网单相断线故障的负序电压电流特征分析及区段定位[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(8):3065-3072.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
王玥婷, 梁中会, 牟欣玮, 等. 考虑分布式能源的配电网断线定位方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(21):131-137.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
王开科, 熊小伏, 肖扬, 等. 基于负序电流的主动配电网单相断线故障保护方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(6):10-18.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
王志远. 有源配电网馈线保护方法研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
常仲学, 宋国兵, 王晓卫. 基于零序电压幅值差的配电网断线识别与隔离[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42(6):135.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
孙朝辉, 鲍有理, 冯靖, 等. 110kV主变高压侧断线故障分析及保护新方法[J]. 电世界, 2021, 62(3):1-5.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
刘王春, 欧朱建, 黄冬冬, 等. 基于PT取电策略的配电架空线路断线故障诊断方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2024, 18(6):131-137.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
马腾. 10kV配电线路断线故障检测与定位研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2013.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
朱传喜, 刘二根. 复变函数与积分变换[M]. 南昌: 江西高校出版社, 2005.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
王宾, 崔鑫. 中性点经消弧线圈接地电力系统弧光高阻接地故障非线性建模及故障解析分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(11):3864-3873.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
IEEE. IEEE guide for the application of neutral grounding in electrical utility systems-Part I:introduction:IEEE Std C62.92.1-2000[S]. New York,NY,US:IEEE, 2000.
|
| [27] |
聂冬, 罗宁昭. 中压舰船电力系统分布电容估计[J]. 船电技术, 2014, 34(2):68-69,80.
|
|
|
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4
京公网安备11010802024360号 京ICP备05059581号-4